The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator![]() The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to interact with servers and devices for certificate management, run SSL discovery and management tasks, and manage synchronization of certificate authorities in remote forests. With the addition of custom extensions, it can provide certificate management capabilities on a variety of platforms and devices (e.g. Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources, Citrix\NetScaler devices, F5 devices, IIS stores, JKS keystores, PEM stores, and PKCS#12 stores) and execute tasks outside the standard list of certificate management functions. It runs on either Windows or Linux servers or Linux containers. can be configured to support client certificate authentication directly by acquiring a certificate for the Keyfactor Command connect service account user or machine account of the orchestrator
The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to interact with servers and devices for certificate management, run SSL discovery and management tasks, and manage synchronization of certificate authorities in remote forests. With the addition of custom extensions, it can provide certificate management capabilities on a variety of platforms and devices (e.g. Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources, Citrix\NetScaler devices, F5 devices, IIS stores, JKS keystores, PEM stores, and PKCS#12 stores) and execute tasks outside the standard list of certificate management functions. It runs on either Windows or Linux servers or Linux containers. can be configured to support client certificate authentication directly by acquiring a certificate for the Keyfactor Command connect service account user or machine account of the orchestrator![]() Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. on the orchestrator and providing it to Keyfactor Command to authenticate the orchestrator.
Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. on the orchestrator and providing it to Keyfactor Command to authenticate the orchestrator.
Complete the following steps and then configure the orchestrator to enable client certificate authentication as per the installation instructions (see -ClientCertificate (Client Certificate Authentication) or Install the Universal Orchestrator on a Linux Server).
Client certificate authentication using this method has the following requirements:
-
The KeyfactorAgents endpoint
 An endpoint is a URL that enables the API to gain access to resources on a server. in Keyfactor Command must be configured to Use SSL.
An endpoint is a URL that enables the API to gain access to resources on a server. in Keyfactor Command must be configured to Use SSL. -
The CA
 A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. CRL
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. CRL A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing Certificate Authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted. endpoints must be reachable by the orchestrator for every CA in the chain for both the CA that issued the SSL
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing Certificate Authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted. endpoints must be reachable by the orchestrator for every CA in the chain for both the CA that issued the SSL TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. certificate on the Keyfactor Command server and the CA that will issue the client authentication certificates.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. certificate on the Keyfactor Command server and the CA that will issue the client authentication certificates.Alternately, you may disable CRL checking when installing each orchestrator (see the --NoRevocationCheck and --no-revocation-check options) or on the Keyfactor Command in the appsettings.json file for the WebAgentServices. By default, this is found in the following path:
C:\Program Files\Keyfactor\Keyfactor Platform\WebAgentServices\Configuration\appsettings.jsonTo disable CRL checking at the server level for the orchestrator endpoint, set CheckAuthCertificateRevocationStatus to false.
{ "ActiveDirectoryEnforced": true, "CheckAuthCertificateRevocationStatus": "true", "ExtensionsDirectory": "Extensions", "MaxRequestSizeKb": "5000", "NLogConfigFile": "Configuration\\NLog_Orchestrators.config", "SqlRetryConfiguration": { "NumberOfTries": "5", "DeltaTime": "00:00:00.5", "MaxTimeInterval": "00:02:00" } } - The CN
 A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com). (common name
A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com). (common name A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com).) of your client authentication certificate (see Acquire a Certificate for Client Certificate Authentication (Optional)) must have a value. Keyfactor recommends using a template
A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com).) of your client authentication certificate (see Acquire a Certificate for Client Certificate Authentication (Optional)) must have a value. Keyfactor recommends using a template A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. configured to set the subject as Supply in the request. The CN of the certificate appears as the identity of the orchestrator in Keyfactor Command.
A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. configured to set the subject as Supply in the request. The CN of the certificate appears as the identity of the orchestrator in Keyfactor Command.
Configure Keyfactor Command for Client Certificate Authentication
First, configure Keyfactor Command to enable client certificate authentication for the orchestrators. Once you do this, all orchestrators connecting to this instance of Keyfactor Command will be required to provide a certificate to authenticate. If you have some orchestrators deployed that do not support certificate authentication (e.g. Java agents), you will need to design a solution with multiple Keyfactor Command servers to support multiple authentication types. Contact your Keyfactor representative for assistance with this.
The KeyfactorAgents endpoint in Keyfactor Command must be configured to Use SSL and the CA CRL endpoints must be reachable by the orchestrator for every CA in the chain for both the CA that issued the SSL certificate on the Keyfactor Command server and the CA that will issue the client authentication certificates.
To configure Keyfactor Command to require client certificate authentication for orchestrators:
- On the Keyfactor Command server, open the Keyfactor Configuration Wizard.
- In the Certificate Authentication section of the Orchestrators tab, check the Enabled box.
- In the Certificate Authentication HTTP Header field, enter a Header Name. For the purposes of this configuration, the value you enter here is not significant, but the field is required, so you must enter something. It will not be used.
- In the Certificate Authentication Username and Certificate Authentication Password fields, enter the credentials for an Active Directory service account for the orchestrator(s).Tip: The service account entered here does not need to match the service account used to authenticate the orchestrator.
- Click Verify Configuration and Apply Configuration.
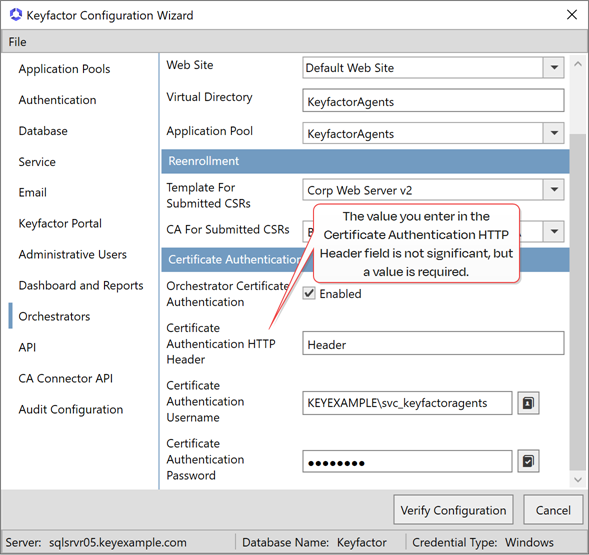
Figure 652: Configure Keyfactor Command for Client Certificate Authentication
Configure Certificate Authentication and SSL Settings in IIS
Make the following changes in the IIS Management console on the Keyfactor Command server:
-
In the IIS Management console, highlight the server name on the left and open Authentication. Make sure Anonymous Authentication is the only enabled method.
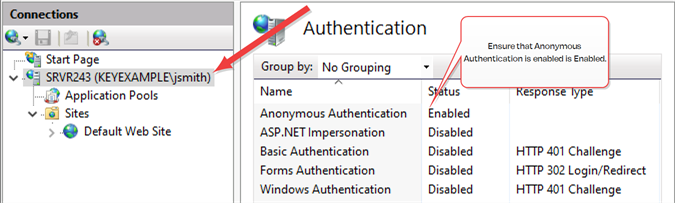
Figure 653: Configure only Anonymous Authentication at the Server Level in IIS
-
In the IIS Management console, highlight Default Web Site (or the web site name you’re using) on the left and open Authentication. Make sure Anonymous Authentication is the only enabled method.
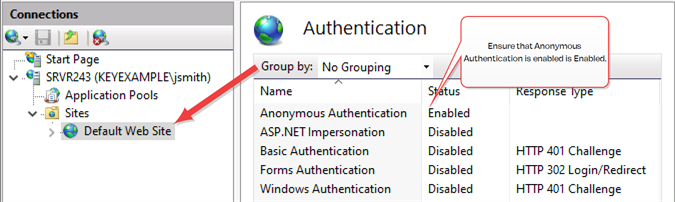
Figure 654: Configure only Anonymous Authentication at the Web Site Level in IIS
-
In the IIS Management console, drill down into sites and into the Default Web Site (or other web site if your Keyfactor Command instance has been installed in an alternate web site). Under the Default Web Site, locate the KeyfactorAgents application and open Authentication for this. Disable all the authentication methods and enable only Anonymous Authentication.
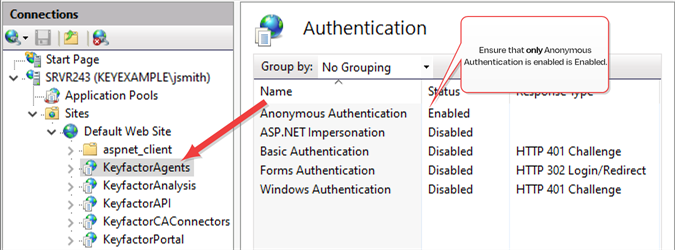
Figure 655: Disable Authentication Methods at the Application Level in IIS
-
In the IIS Management console, open SSL Settings for the KeyfactorAgents application. Check the Require SSL box and select either Require or Accept for Client certificates.
Important: Only selected Require if your are only using orchestrators that support client certificate authentication and plan to configure all of them for certificate authentication.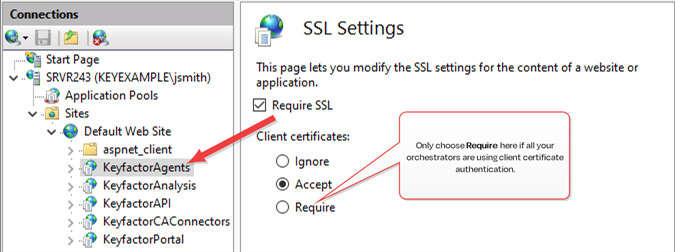
Figure 656: Configure SSL Settings in IIS for Client Certificate Authentication
Tip: If your KeyfactorAgents endpoint is running on a standalone server with no other Keyfactor roles, you may also configure your server to Require or Accept for Client certificates at the Default Web Site level. It is good security practice to check the Require SSL box. If your KeyfactorAgents endpoint is running on a server with other Keyfactor roles, you do not need to accept client certificates at this level and should not require them at this level.
Was this page helpful? Provide Feedback