The following error conditions and general troubleshooting tips may be helpful in resolving issues with the Keyfactor Command server. Generally speaking, issues on installation or upgrade are often related to SQL connectivity or permissions. When Active Directory is used as the identity provider, certificate enrollment![]() Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). issues are often related to Kerberos configuration problems.
Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). issues are often related to Kerberos configuration problems.
 IIS Authentication Configuration
IIS Authentication Configuration
If authentication is not working as expected, it can be helpful to review whether the authentication configuration in IIS is correct for the identity provider you have configured. The correct IIS authentication configurations are:
-
If you’re using an identity provider other than Active Directory, the KeyfactorAgents, KeyfactorAPI, and KeyfactorPortal virtual directories should be set with Anonymous Authentication enabled and all other authentication methods disabled.
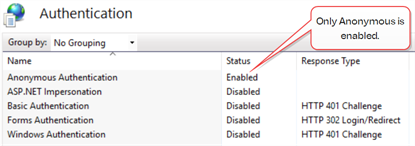
Figure 419: IIS Authentication for Virtual Directories with an Identity Provider Other Than Active Directory
-
If you’re using Active Directory, the default configuration for the KeyfactorAgents, KeyfactorAPI, and KeyfactorPortal virtual directories is Anonymous Authentication, Basic Authentication, and Windows Authentication enabled. You have the option to disable either Basic Authentication or Windows Authentication for the KeyfactorPortal and KeyfactorAPI virtual directories to force users to login with only one of these methods, if desired. The KeyfactorAgents virtual directory may be configured to Anonymous Authentication only if certificate-based authentication is in use for your orchestrators (see Appendices).
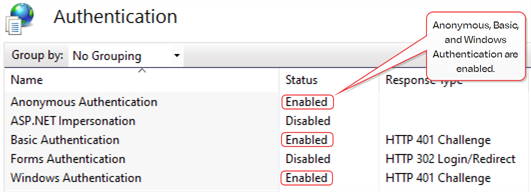
Figure 420: IIS Authentication for Virtual Directories with Active Directory
Note: If you make customizations to the authentication settings such as disabling Basic Authentication for the KeyfactorPortal virtual directory and subsequently enable the OAuth option in the configuration wizard, these customizations will be lost. - The KeyfactorAnalysis and KeyfactorProxy virtual directories are set with only Anonymous Authentication for all identity provider configurations.
- At the site level (e.g. Default Web Site), only Anonymous Authentication should be enabled for all identity provider configurations.
 Debug Logging and Error Messages
Debug Logging and Error Messages
It is often helpful to enable debug logging on the server. For information on configuring this, see Editing NLog.
Once the logging is set at debug or trace level, it can be helpful to watch the logs live while activity is going on. There are tools on Windows with functionality similar to the Linux tail function to watch the log in real time. Notepad++, for example, has this functionality built in. Be sure to review all the logs that could be relevant. For example, installation and configuration messages are found in the configuration log. Messages related to using the Management Portal can be found in both the portal log and the Keyfactor API![]() A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. log.
A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. log.
Some messages in the Keyfactor API and orchestrators API logs include a correlation ID that helps to identify log messages that originated from the same request. The correlation ID is a randomly generated GUID that often appears just after the date in the log entry (C282ACA1-DED5-4F2E-B83B-F3F9E865E371 in the following example) and is the same for all log messages for the given request until the request completes.
2022-09-13 04:51:18.6884 C282ACA1-DED5-4F2E-B83B-F3F9E865E371 CSS.CMS.Web.KeyfactorApi.Controllers.Enrollment.Enrollment2Controller [Trace] - Starting PFX Enrollment Process 2022-09-13 04:51:19.0477 C282ACA1-DED5-4F2E-B83B-F3F9E865E371 Keyfactor.Command.Workflows.Engine.WorkflowGraph [Error] - Invalid O provided: Value must be Key Example, Inc or Key Example.
 General Errors
General Errors
Below are some possible errors you might encountered and some suggested troubleshooting tips or solutions.
You many encounter this error when trying to install or upgrade to Keyfactor Command version 10 or later:
2022-03-04 09:58:55.7262 CSS.CMS.Install.ConfigurationWizard.ViewModels.DatabaseViewModel [Error] - Unable to configure database 2022-03-04 09:58:55.9821 CSS.CMS.Install.ConfigurationWizard.ViewModels.DatabaseViewModel [Error] - An error occurred while preparing the database at CSS.CMS.Install.ConfigurationWizard.ViewModels.DatabaseViewModel.b(Object A_0, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs A_1) A connection was successfully established with the server, but then an error occurred during the login process. (provider: SSL Provider, error: 0 - The certificate chain was issued by an authority that is not trusted
Keyfactor Command version 10 requires an encrypted connection to the SQL server. If the SQL server is not configured correctly to receive a secure connection (is not configured with a valid certificate that is trusted by the Keyfactor Command server), you may receive this message.
For information about configuring TLS![]() TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. for SQL server, see:
TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. for SQL server, see:
You may encounter this error on an enrollment when the CA![]() A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. rejects the request. If the request is clearly not excessively long, review the request for invalid characters. Be sure to also check the default subject (see the Subject Format application setting on the Application Settings: Enrollment Tab and the subject defaults in certificate templates for both Configuring System-Wide Settings and Enrollment Defaults Tab). Quotation marks should not be used in the fields of the default subject except in the case where these are part of the desired subject value, as they are processed as literal values. This is a change from earlier versions of Keyfactor Command where quotation marks were used around fields containing embedded commas.
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. rejects the request. If the request is clearly not excessively long, review the request for invalid characters. Be sure to also check the default subject (see the Subject Format application setting on the Application Settings: Enrollment Tab and the subject defaults in certificate templates for both Configuring System-Wide Settings and Enrollment Defaults Tab). Quotation marks should not be used in the fields of the default subject except in the case where these are part of the desired subject value, as they are processed as literal values. This is a change from earlier versions of Keyfactor Command where quotation marks were used around fields containing embedded commas.
This error can also appear if a Microsoft CA receives an enrollment request with no subject at all.
You may encounter this error in the Keyfactor Command logs when trying to connect to the Management Portal. This can indicate that one or more of the service accounts configured to run the IIS application pools for Keyfactor Command do not have private key![]() Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. permissions to the certificate used to provide application-level encryption in Keyfactor Command (see Application-Level Encryption
Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. permissions to the certificate used to provide application-level encryption in Keyfactor Command (see Application-Level Encryption
Category: Microsoft.AspNetCore.DataProtection.KeyManagement.KeyRingProvider
EventId: 48
An error occurred while reading the key ring.
Exception:
System.Exception: Unable to decrypt enveloped PKCS7 data
You may encounter this error either in the Keyfactor CommandManagement Portal or when submitting a Keyfactor API request. This error is typically not accompanied by any error in the Keyfactor Command logs. This error can occur if the IIS WebDAV Publishing feature is installed on the Keyfactor Command server. Keyfactor Command is not compatible with this IIS feature. Uninstall the WebDAV Publishing feature, reboot if required, and try your command again.
This error may appear during certificate enrollment against a certificate authority![]() A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. running the Keyfactor CA Policy Module if the license for the policy module has expired. See License Expiration Monitoring and Rotation for license update information.
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. running the Keyfactor CA Policy Module if the license for the policy module has expired. See License Expiration Monitoring and Rotation for license update information.
You may encounter an error similar to the following in the EJBCA log (not one of the Keyfactor Command logs) on a certificate enrollment if you make an enrollment attempt through Keyfactor Command using an EJBCA certificate profile configured with one or more custom certificate extensions that do not have a matching enrollment field configuration in Keyfactor Command. This may occur when using templates intended for use with the Keyfactor Windows Enrollment Gateway with incomplete Keyfactor Command configuration.
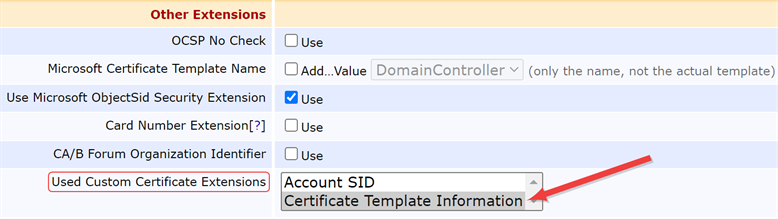
Figure 421: EJBCA Certificate Profile Custom Certificate Extensions
To operate correctly with Keyfactor Command, the profiles in EJBCA will need to be configured to not expect extension data. If you’re using the the Keyfactor Windows Enrollment Gateway and wish to do direct enrollments in Keyfactor Command for your EJBCA CA as well as through the Keyfactor Windows Enrollment Gateway, you will need a separate set of certificate profiles in EJBCA that are not configured to expect extension data with the request to use for direct enrollment from Keyfactor Command.
If you encounter a web server error (e.g. a 502 error) while authenticating with an identity provider other than Active Directory or across the entire Keyfactor Command product once you have authenticated with an identity provider other than Active Directory, it can be helpful to enable extended logging for the ClaimsProxy log. For more information, see Table 87: NLog.config Files for Keyfactor Command.
 Certificate Validation Errors
Certificate Validation Errors
On the Validation tab of the certificate details you will sometimes see a fail result for some of the validation tests. The following are some possible reasons why this might occur.
-
If you see both Full Chain and CRL Online in a fail state, this generally indicates that you have not imported the root and/or intermediate certificate for the certificate into the appropriate store on the Keyfactor Command server (see Configure Certificate Chain Trusts for CAs in the Keyfactor Command Server Installation Guide).
-
If you see just CRL Online in a fail state, this generally indicates that the Certificate Revocation List
 A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing Certificate Authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted. (CRL
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing Certificate Authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted. (CRL A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing Certificate Authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted.) for the CA could not be reached.Important: Because a “+” (plus sign) in a URL can represent either a space or a “+” Keyfactor Command has chosen to read “+” as a space. For CRL URLs that require a “+” (plus sign), rather than a space, replace plus signs in your CRL's URL with “
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing Certificate Authority (CA) before their scheduled expiration date and should no longer be trusted.) for the CA could not be reached.Important: Because a “+” (plus sign) in a URL can represent either a space or a “+” Keyfactor Command has chosen to read “+” as a space. For CRL URLs that require a “+” (plus sign), rather than a space, replace plus signs in your CRL's URL with “%2B”. Only replace the plus signs you don't wish to be treated as a space. -
If you see Revocation Status in a fail state but CRL Online is in a pass state, this can indicate that the CRL is accessible but expired, that the CRL is not fully configured, or that the Authority Information Access
 The authority information access (AIA) is included in a certificate--if configured--and identifies a location from which the chain certificates for that certificate may be retrieved. (AIA
The authority information access (AIA) is included in a certificate--if configured--and identifies a location from which the chain certificates for that certificate may be retrieved. (AIA The authority information access (AIA) is included in a certificate--if configured--and identifies a location from which the chain certificates for that certificate may be retrieved.) for the CA has not been configured correctly or could not be reached.
The authority information access (AIA) is included in a certificate--if configured--and identifies a location from which the chain certificates for that certificate may be retrieved.) for the CA has not been configured correctly or could not be reached.For EJBCA CAs, CRLs and AIA need to be configured both at the CA level and at the certificate profile level. One way to do this is:
- AIA: Set the path to the AIA in the CA issuer Default URI field in the CA. You can find this on the Fetch CA certificates page of your EJBCA public web. Check both the Authority Information Access box and the Use CA defined CA issuer box in each certificate profile.
- CRL: Set the path to the CRL distribution point (CDP) in the Default CRL Distribution Point field in the CA. If appropriate for your environment, set also the Default CRL Issuer and/or Default Freshest CRL Distribution Point (delta CRLs). Check both the CRL Distribution Points box and the Use CA defined CRL Distribution Point box in each certificate profile.
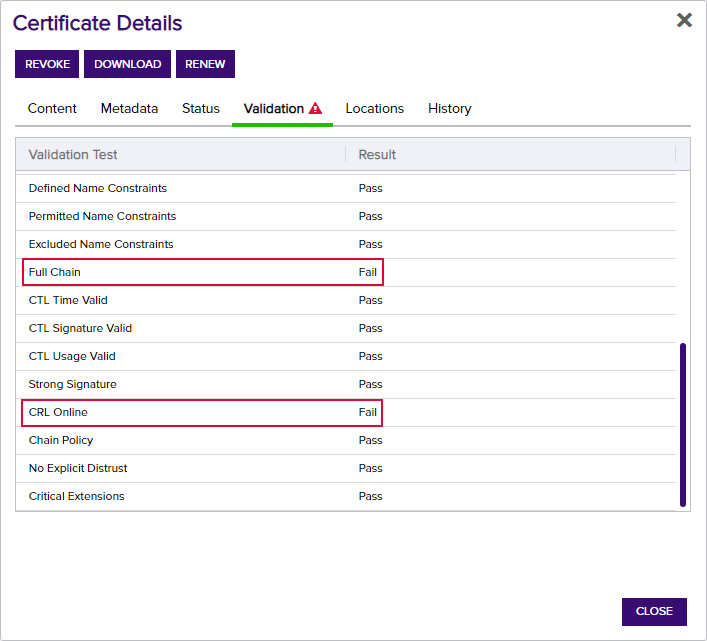
Figure 422: Certificate Validation Fails for Full Chain and CRL Online
 Slow SSL Jobs
Slow SSL Jobs
If SSL![]() TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. jobs are taking longer to complete than expected and you check the log on the orchestrator
TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. jobs are taking longer to complete than expected and you check the log on the orchestrator![]() Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. and find messages similar to the following:
Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. and find messages similar to the following:
2021-08-24 17:22:48.4463 Keyfactor.WindowsAgent.Jobs.SSL.SslDiscovery [Error] - Error while sending SSL Batch for audit id 158558. Check the CMS Server log for more details. Response status code does not indicate success: 413 (Request Entity Too Large).
at System.Net.Http.HttpResponseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCode() at Keyfactor.WindowsAgent.Jobs.GenericJobExecutor`7.f.h()
2021-08-24 17:22:48.4463 Keyfactor.WindowsAgent.Jobs.SSL.SslDiscovery [Info] - Splitting endpoint result batch of 29 into smaller pieces and retrying
You may want to make modifications to the IIS maximum request size settings on your Keyfactor Command server to allow it to accept larger incoming pieces of content to streamline SSL scanning. You can do this using the configuration editor built into the IIS management console. Make the setting changes at the Default Web Site level (or other web site, if you installed your Keyfactor Command in an alternate web site). There are three settings to change:
- system.webServer/ security/ requestFiltering/ requestLimits/ maxAllowed ContentLength
- system.webServer/ serverRuntime/ uploadRead AheadSize
- system.web/ httpRuntime/ maxRequest Length
Set each system.webServer value to at least 1,000,000 bytes for best SSL scanning performance. The default value of 4096 KB for the maxRequestLength will probably be sufficient for SSL scanning in most environments, but if it has been reduced in your environment, you may need to increase it. (The system.webServer values are set in bytes while the system.web values are set in kilobytes.) If you are scanning networks with especially large numbers of returned certificates, you may need to increase all these values. Monitor the orchestrator logs after modifying the values to confirm that you have achieved the desired effect.
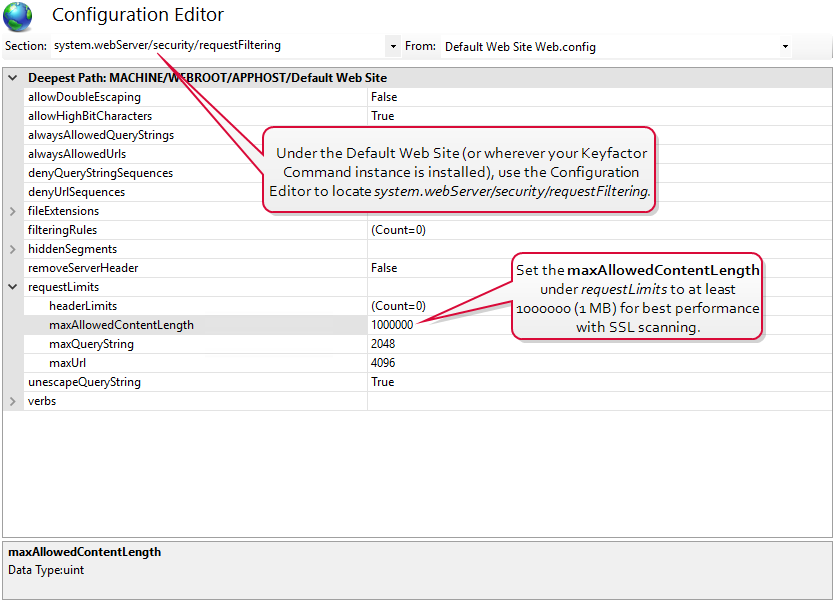
Figure 423: Modify IIS Settings for SSL Scanning: maxAllowedContentLength
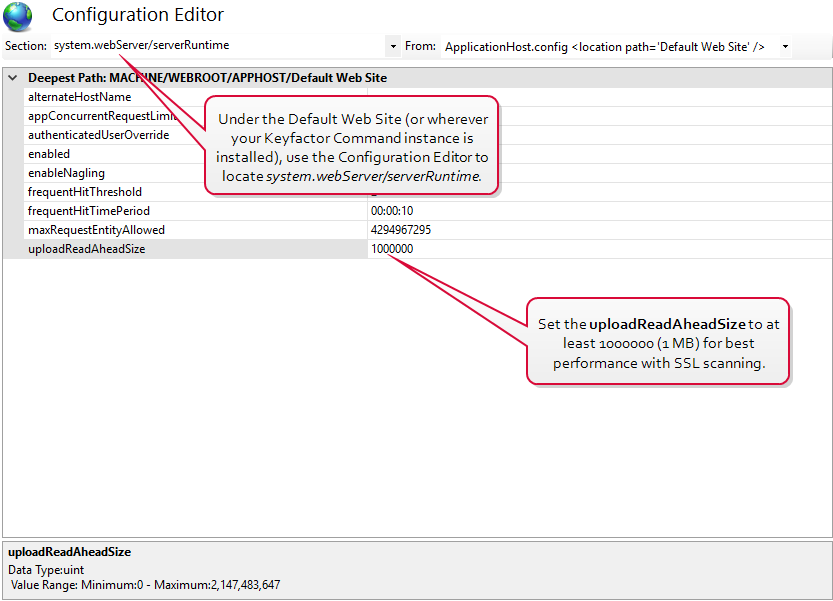
Figure 424: Modify IIS Settings for SSL Scanning:uploadReadAheadSize
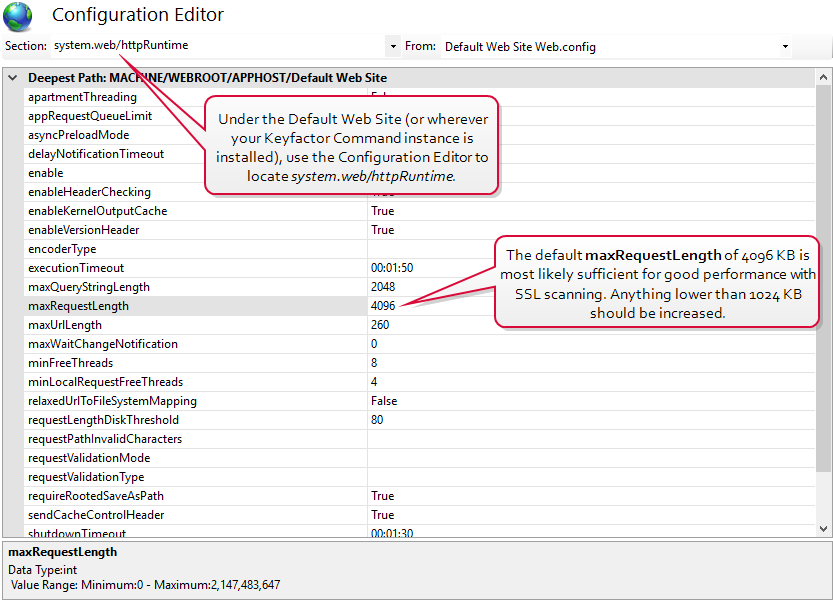
Figure 425: Modify IIS Settings for SSL Scanning: maxRequestLength