Permissions on PAM![]() PAM (Privileged Access Management): Controls privileged access by vaulting credentials, enforcing least-privilege/just-in-time access, rotating secrets, and auditing sessions. Across Keyfactor products, PAM protects diverse sensitive operations and secrets—for example certificate stores and CA credentials—via built-in or third-party providers; external integrations are delivered as custom PAM extensions (several published on Keyfactor’s public GitHub). can be controlled at two levels—system-wide and on a provider-by-provider basis. When designing a PAM permission scheme, you may use entirely system-wide permissions or you may use a combination of system-wide permissions and provider-level permissions. Both system-wide and provider-level permissions are configured through Security Roles (see Security Role Operations).
PAM (Privileged Access Management): Controls privileged access by vaulting credentials, enforcing least-privilege/just-in-time access, rotating secrets, and auditing sessions. Across Keyfactor products, PAM protects diverse sensitive operations and secrets—for example certificate stores and CA credentials—via built-in or third-party providers; external integrations are delivered as custom PAM extensions (several published on Keyfactor’s public GitHub). can be controlled at two levels—system-wide and on a provider-by-provider basis. When designing a PAM permission scheme, you may use entirely system-wide permissions or you may use a combination of system-wide permissions and provider-level permissions. Both system-wide and provider-level permissions are configured through Security Roles (see Security Role Operations).
System Settings → Privileged Access Management
System-wide PAM permissions are controlled using the Privileged Access Management role permission. These permissions control which users have access to viewing and managing any PAM providers you will use in your Keyfactor Command implementation.
Figure 431: Global PAM Permissions
PAM provider-level permissions are controlled with the optional provider-by-provider permissions on the PAM Provider Permissions tab of the Security Role Information dialog. The permissions set on the PAM Provider Permissions tab allow a user to access only the referenced PAM provider when selected.
Any PAM providers that do not have provider-level permissions applied fall back to the system-wide permissions, if any system-wide permissions have been set for that security role.
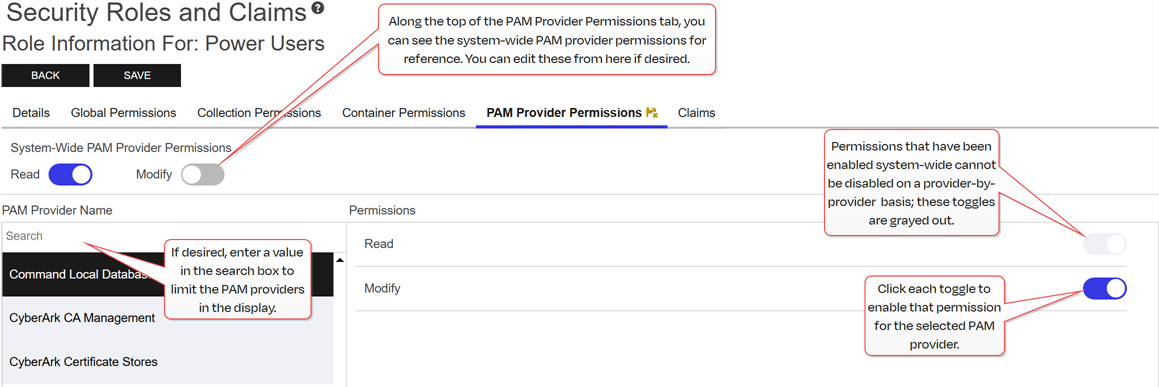
Figure 432: PAM Provider Permissions
PAM permissions can be granted system-wide or on a provider basis. Both options share the same permission options (see Privileged Access Management (PAM)).
Was this page helpful? Provide Feedback