Keyfactor ACME Architecture
The elements of Keyfactor ACME are:
-
Microsoft SQL Server
- The Keyfactor ACME SQL database holds the Keyfactor ACME accounts, application settings, certificates, orders, authorizations, nonces, and secrets.
- The Keyfactor ACME database is a separate schema that can be loaded on the same database server as Keyfactor Command.
-
Multiple Keyfactor ACME servers can use a common database to allow for load balancing. For more information on configuring Keyfactor ACME load balancing, see Configuring Keyfactor ACME for Load Balancing on Windows.
-
By default, sensitive data—such as EAB HMAC keys—is securely stored in the Keyfactor ACME database using SQL encryption. However, an additional layer of security can be added with application-level encryption (see Application-Level Encryption).
-
For Windows installs, when using SQL Authentication to configure a Keyfactor ACME server, the current user and the application pool user become the only users that can run any of the Command Line Tool commands. When Windows authentication is used, the application pool user is granted permissions to access the SQL Server and the Keyfactor ACME database.
-
Authentication and Authorization
Keyfactor ACME uses authentication for two purposes:
-
Client Authentication: To authenticate clients to the Keyfactor ACME server when acquiring EAB keys.
For his purpose, Keyfactor ACME uses OAuth.
-
Server Authentication: To authenticate Keyfactor ACME to Keyfactor Command when enrolling for certificates.
For this purpose Keyfactor ACME can use OAuth, Basic Authentication, or Windows Authentication (installations on Windows only) depending on the configuration of the Keyfactor Command instance. If OAuth is used for server authentication, the identity provider can be a different provider from that used for client authentication.
The client account configured to authenticate to Keyfactor Command must have Certificates > Enrollment > Csr and Certificates > Enrollment > Read permissions in Keyfactor Command.
During configuration, authentication to and authorization for the Keyfactor Command server are verified. The authentication type enabled on the Keyfactor Command server is validated using the provided URL. If the authentication type provided does not match the authentication type on the Keyfactor Command, the configuration process will not continue.
Important: The OAuth identity provider used to authenticate to Keyfactor Command must be defined as an identity provider in Keyfactor Command.
-
- The Keyfactor API is used to communicate between Keyfactor ACME and Keyfactor Command to perform the certificate request, renew, and revocation tasks.
- The hostname of the Keyfactor ACME server is used to build the URLs to which the ACME client can make calls. For more information on configuring Keyfactor ACME load balancing, see Configuring Keyfactor ACME for Load Balancing on Windows.
- A virtual directory is created on the web server using Keyfactor ACME authentication. The default value is ACME (e.g. https://acmeserver.keyexample.com/ACME), but that can be changed by passing another value during configuration.
- On Windows, an application pool user identity is used to run the Keyfactor ACME application.
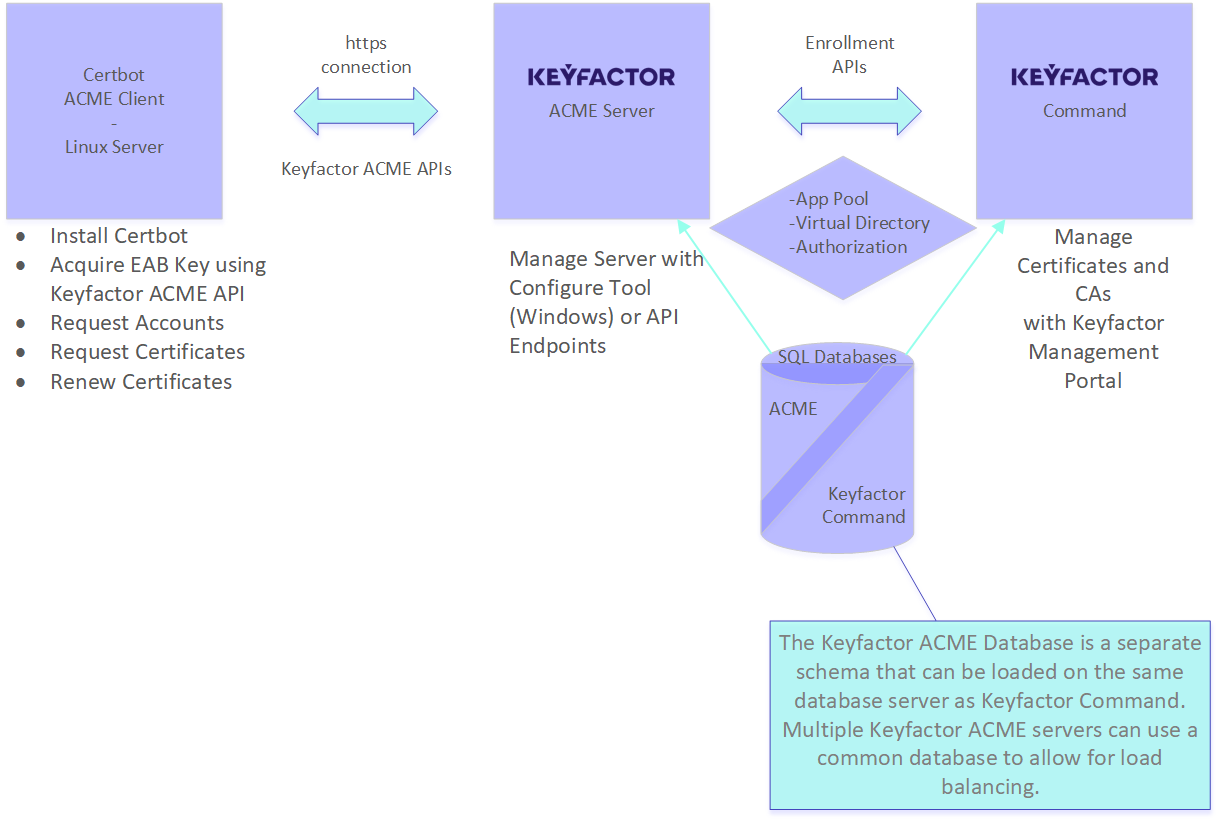
Figure 1: Keyfactor ACME Architecture
Was this page helpful? Provide Feedback