Request a Certificate
When you request a certificate through Keyfactor ACME, it is requested via the Keyfactor ACME enrollment![]() Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). API
Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA). API![]() An API is a set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. and validated with your Certbot account and the ACME configuration details. A regular enrollment request is then issued in Keyfactor Command and will display in the certificate search in the Keyfactor Command Management Portal.
An API is a set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. and validated with your Certbot account and the ACME configuration details. A regular enrollment request is then issued in Keyfactor Command and will display in the certificate search in the Keyfactor Command Management Portal.
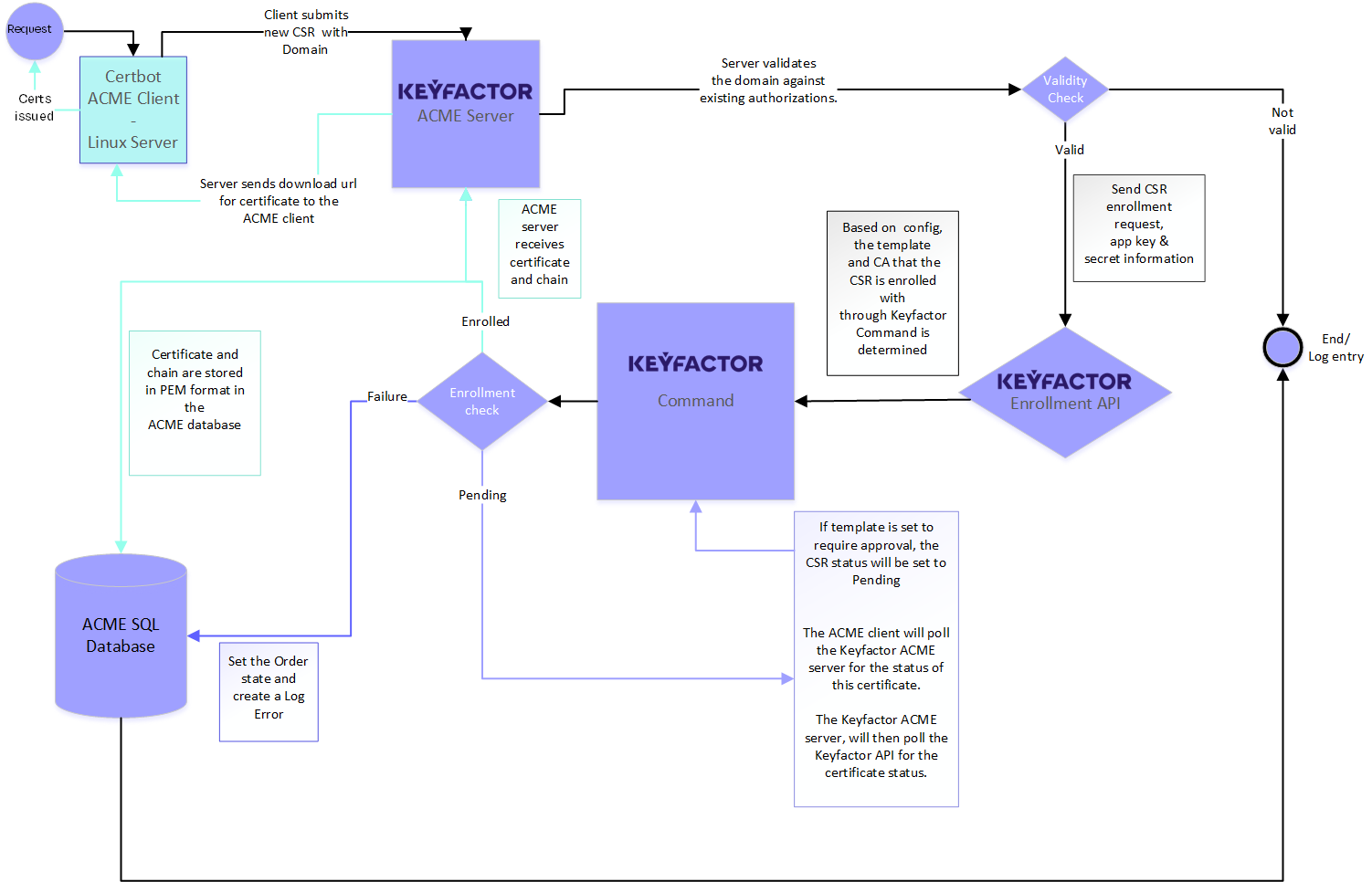
Figure 17: Request a Certificate using Keyfactor ACME Workflow
Certbot has multiple parameters to specify differing options. The parameter![]() A parameter or argument is a value that is passed into a function in an application. values you will need to make a simple request for a certificate from your Keyfactor ACME server and Keyfactor Command are shown in Table 41: Request Certificate Parameters. Your Certbot implementation may require a different web server plugin than the popular ones shown in this table.
A parameter or argument is a value that is passed into a function in an application. values you will need to make a simple request for a certificate from your Keyfactor ACME server and Keyfactor Command are shown in Table 41: Request Certificate Parameters. Your Certbot implementation may require a different web server plugin than the popular ones shown in this table.
Table 41: Request Certificate Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| --apache | Specify that Certbot make the request using the Apache plugin and automatically install the certificate. |
| --elliptic- curve | Specify the elliptic curve for a request with an ECC key type. |
| --key-type |
Specify the key type for the certificate request (e.g. rsa, ecdsa). Note: Beginning with version 2.0, Certbot issues ECDSA (secp256r1) certificates by default. In many cases, a web server certificate template is configured for RSA encryption and so will not be compatible with this default. You may either configure the Keyfactor ACME server with a certificate template that supports ECDSA (secp256r1) or specify an appropriate key type and key size in your Certbot requests.
|
| --nginx | Specify that Certbot make the request using the nginx plugin and automatically install the certificate. |
| --rsa- key- size | Specify the key size for a request with an RSA key type. |
| --server |
The URL of the Keyfactor ACME server / the virtual directory specified in the Keyfactor ACME configuration. For example: https://acmesrvr93.keyexample.com/ACME
|
| --standalone | Use standalone mode to make the request. This option assumes that no other web server is running on the server from which the Certbot request is issued. A miniature web server is started just for the duration of the request to satisfy Certbot's need for a web server. |
| -d |
The domain name for the certificate. The domain(s) must be on the list provided to Keyfactor ACME by running the configuration tool with the verb identifiers (see Validators and the Identifiers Command) unless you have disabled this option. For example: appsrvr162.keyexample.com |
| REQUESTS_ CA_ BUNDLE= /etc/ssl /certs /ca-certificates.crt |
Specify the location of the trusted root certificate on the Linux server by providing the environment variable before Certbot requests. Note: The file provided should be the one created by running update-ca-certificates using your CA chain certificates.
|
Example for Standalone:
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt certbot --standalone --server https://acme93.keyexample.com/ACME -d appsrvr18.keyexample.comREQUESTS_CA![]() A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA._BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt certbot certonly --standalone --server https://acme93.keyexample.com/ACME -d appsrvr18.keyexample.com
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA._BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt certbot certonly --standalone --server https://acme93.keyexample.com/ACME -d appsrvr18.keyexample.com
Example for Standalone with IP address SANs submitted in a script:
-
Create an input configuration file containing the subject and SAN values:
Copy[req]
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = req_ext
prompt = no
[req_distinguished_name]
CN = mysubject.keyexample.com
C = US
ST = Ohio
L = Independence
O = Key Example
OU = IT
[req_ext]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = 192.168.12.148
IP.2 = 2001:db8:abcd:cdef:1:1:1:1
DNS.1 = mysan.keyexample.com - Create a script to submit the request to the Keyfactor ACME server, calling the configuration file:
-
Copy
enroll-script.sh
#!/bin/bash
# Enroll for an SSL cert with the specified Keyfactor ACME server.
# Usage: .\scriptname.sh
acmehost=acme93.keyexample.com
openssl genrsa -out keypair.pem 2048
openssl req -new -key keypair.pem -out ip-csr.csr -config ip-csr.cnf
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt certbot certonly --standalone --server "https://$acmehost/ACME" -v --csr ip-csr.csr - Execute the script.
Example for Apache:
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt certbot --apache --server https://acme93.keyexample.com/ACME -d appsrvr27.keyexample.comExample for Nginx:
REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt certbot certonly --nginx --server https://acme93.keyexample.com/ACME -d appsrvr162.keyexample.comExpected Results in Linux for Nginx:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
http-01 challenge for appsrvr162.keyexample.com
Waiting for verification...
Cleaning up challenges
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/appsrvr162.keyexample.com-0001/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/appsrvr162.keyexample.com-0001/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2023-09-14. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot
again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
"certbot renew"
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-leWas this page helpful? Provide Feedback