Typically with services that use a forwarding proxy, there is a specific proxy configuration done within the application, but the Universal Orchestrator![]() Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. doesn't have such a configuration. Instead, it makes use of an environment variable to retrieve this information on either Windows or Linux.
Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. doesn't have such a configuration. Instead, it makes use of an environment variable to retrieve this information on either Windows or Linux.
On Windows, configure a system environment variable of either HTTP_PROXY or HTTPS_PROXY (this is not case sensitive on Windows) pointing to your proxy's URL, including port, then restart the Universal Orchestrator service if the orchestrator is already installed.
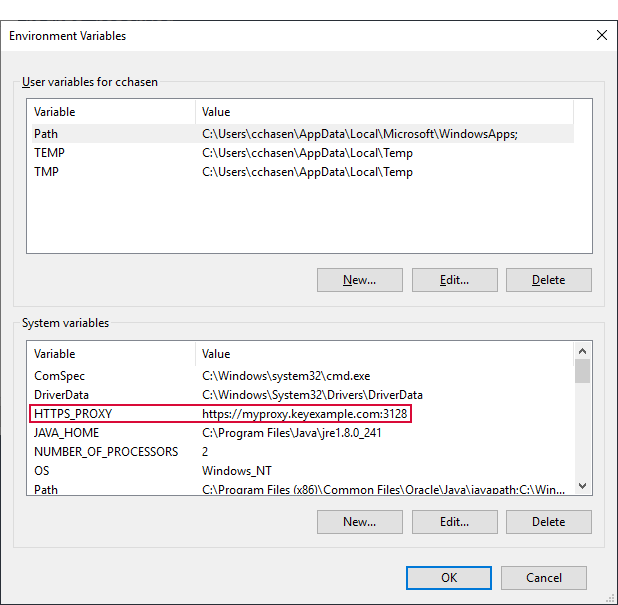
Figure 638: System Environment Variable to Define a Proxy URL for Use by the Universal Orchestrator on Windows
On Linux, there are multiple approaches to setting an environment variable. One method for setting a system-wide environment variable that will be retained after reboot is to add an environment variable statement to the /etc/environment file using a command similar to the following (as root):
After setting the environment variable, restart the Universal Orchestrator service if the orchestrator has already been installed.
In the [Service] section, add an entry similar to the following for each proxy you wish to set:
For example:
[Unit]
Description=Keyfactor Orchestrator (default)
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dotnet ./Orchestrator.dll
Environment=https_proxy=https://myproxy.keyexample.com:3128
Environment=http_proxy=http://myproxy.keyexample.com:8080
WorkingDirectory=/opt/keyfactor/orchestrator
User=keyfactor-orchestrator
Group=keyfactor-orchestrator
Restart=on-failure
SyslogIdentifier=keyfactor-orchestrator
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target