On the Service Account Keys page, an administrator can view and download existing keys issued for service accounts and generate new key pairs.
- Uses the Keyfactor Command Management Portal to create a new key pair (see Creating a Service Account Key). She enters the following information in the form:
- Key Type: Ed25519
- Key Length: 256
Server Group: Server Group One
The server group to which the Linux servers belong that the public key
 In asymmetric cryptography, public keys are used together in a key pair with a private key. The private key is retained by the key's creator while the public key is widely distributed to any user or target needing to interact with the holder of the private key. will be distributed to.
In asymmetric cryptography, public keys are used together in a key pair with a private key. The private key is retained by the key's creator while the public key is widely distributed to any user or target needing to interact with the holder of the private key. will be distributed to.Client Hostname: appsrvr75
The Linux server on which the private key
 Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. of the SSH key pair will be download. This does not need to be a server added for management in Keyfactor Command and is a field for reference only.
Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. of the SSH key pair will be download. This does not need to be a server added for management in Keyfactor Command and is a field for reference only.Username: svc_greenchicken
The service account name the application uses. This does not need to match the Linux logon name the application uses. This username together with the client hostname
 The unique identifier that serves as name of a computer. It is sometimes presented as a fully qualified domain name (e.g. servername.keyexample.com) and sometimes just as a short name (e.g. servername). make the full user name for the service account key within Keyfactor Command svc_greenchicken@appsrvr75.
The unique identifier that serves as name of a computer. It is sometimes presented as a fully qualified domain name (e.g. servername.keyexample.com) and sometimes just as a short name (e.g. servername). make the full user name for the service account key within Keyfactor Command svc_greenchicken@appsrvr75.Email: pkiadmins@keyexample.com
The group responsible for rotating the key when it reaches the end of its lifetime. This group will receive email alerts when the key is becoming stale.
Passphrase: A complex password used to secure the private key.
She needs to record the passphrase because this will be needed by application to access the private key.
- Comment: Green Chicken Service
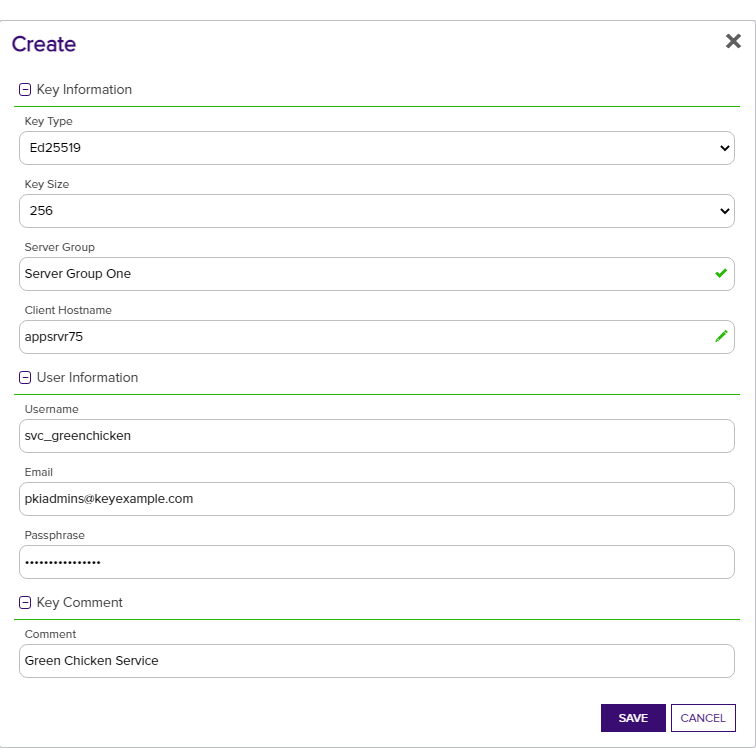
Figure 303: Acquire a New Service Account Key
- Downloads the SSH private key on the server doing the log collection
 The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports)., from which the SSH connections will be made to collect logs.
The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports)., from which the SSH connections will be made to collect logs. Uses the Management Portal to map the new public key for the full service account user name (svc_greenchicken@appsrvr75) to the Linux logons for the service on the servers from which the logs will be collected (see Editing Access to an SSH Server Group).
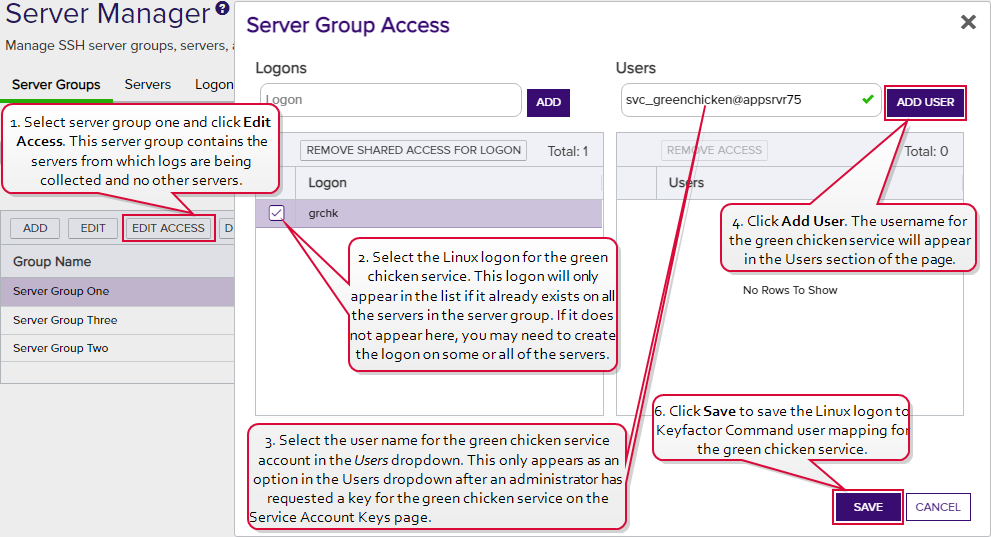
Figure 304: Map Service Account Public Key to Logon
Note: The servers that the logs will be collected from are organized into a server group so the administrator can create logons and map the service account key using the Access Management option on the Server Group page. If the servers were in different server groups or the server group contained servers which should not be updated with logons and keys for the green chicken service, the administrator would need to create the logons and mappings separately for each server using the Access Management option on the Servers page (see Editing Access to an SSH Server).- Waits for the public key to be published to the servers. The time that this takes depends on the frequency of the server group synchronization schedule (see Adding Server Groups).
- Confirms that the service is able to successfully connect using secured SSH.
You can also find the help icon at the top of the page next to the Log Out button. From here you can choose to open either the Keyfactor Command Documentation Suite at the home page or the Keyfactor API Endpoint Utility.