Certificate Permissions
Permissions on certificates and their collections are controlled at two levels—globally at the certificate level and on a collection![]() The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports).-by-collection basis. Global certificate permissions are controlled on the Certificates role permissions. Global collection permissions are controlled with the Certificate Collections role Modify permission used in conjunction with the collection-by-collection basis permissions controlled on the Collections Permissions tab.
The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports).-by-collection basis. Global certificate permissions are controlled on the Certificates role permissions. Global collection permissions are controlled with the Certificate Collections role Modify permission used in conjunction with the collection-by-collection basis permissions controlled on the Collections Permissions tab.
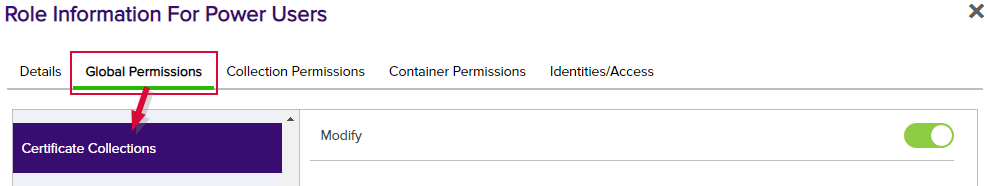
Figure 347: Certificate Collection Global Permissions
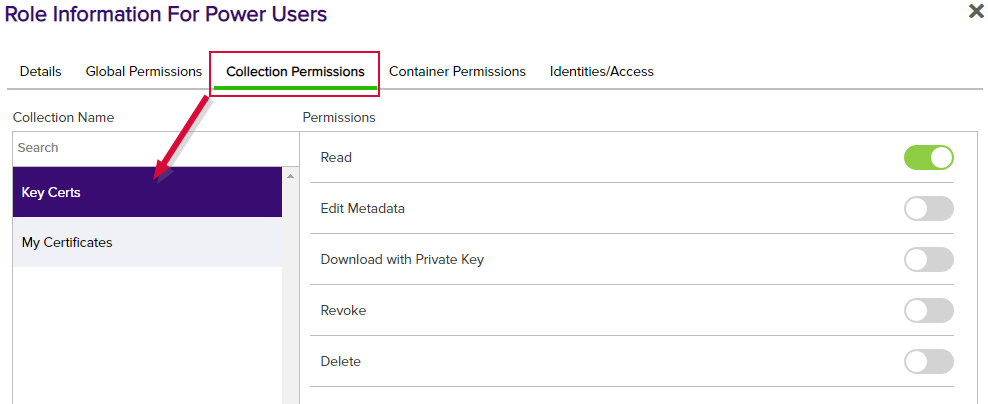
Figure 348: Certificate Collection per Collection Permissions
Certificate-related permissions can be granted globally (per global permissions—Certificates) or on a collection basis (per the Certificate Permissions tab). Both options share the same permissions options, except global certificate permissions have the additional role permissions of Import Private Key and Import, which can not be assigned at the collection level.
Users with global Read role permission for Certificates can browse to Certificate Search in the Management Portal and view all saved certificate collections. They can view any certificate in the Keyfactor Command database and are not limited to just those returned by select collections. Users with this permission can view the certificates returned by searches and open the details of the certificates.
Users with collection-level Read role permissions on a collection will see the collections to which they have been granted access appear on the Certificate Collections menu (if they have been configured to appear on the menu (see Certificate Collection Manager). The users will be able to view all the certificates in the collections and open the details of the certificates.
The certificate operations available to these users are:
- Add to Certificate Store (Also requires the Read and Schedule Certificate Store Management permissions)
- Edit
- Download
- Get CSV
- Identity Audit (Also requires the Read Security Settings permission)
- Include Revoked checkbox
- Include Expired checkbox
- Renew (Also requires the Read and Schedule Certificate Store Management permissions)
- Remove from Certificate Store (Also requires the Read and Schedule Certificate Store Management permissions)
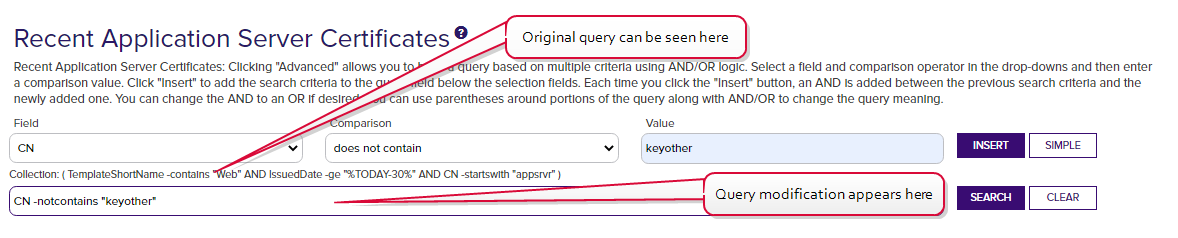
In the case of collections, users will be able to further refine the collection query by including additional selection criteria in the query field, but these are used in addition to the base query. Users are not allowed to clear the base query for the collection, which is displayed above the query field. For example, for the collection shown in Figure 349: Collection with Read Collection-Level Security, if the user added this in the query field:
The query would return all the certificates issued in the last 30 days with the string "appsrvr" in the CN![]() A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com). using a template
A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com). using a template![]() A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. referencing "Web" but without the string "keyother" in the CN—in other words, the web server certificates for application servers issued in the last 30 days for the keyexample.com domain but not the web server certificates for application servers issued in the last 30 days for the keyother.com domain.
A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. referencing "Web" but without the string "keyother" in the CN—in other words, the web server certificates for application servers issued in the last 30 days for the keyexample.com domain but not the web server certificates for application servers issued in the last 30 days for the keyother.com domain.
Users with the Edit Metadata role permission for Certificates can edit the certificates in the Certificate Details dialog (only information on the metadata![]() Metadata provides information about a piece of data. It is used to summarize basic information about data, which can make working with the data easier. In the context of Keyfactor Command, the certificate metadata feature allows you to create custom metadata fields that allow you to tag certificates with tracking information about certificates. tab can be edited) for which they have been given access.
Metadata provides information about a piece of data. It is used to summarize basic information about data, which can make working with the data easier. In the context of Keyfactor Command, the certificate metadata feature allows you to create custom metadata fields that allow you to tag certificates with tracking information about certificates. tab can be edited) for which they have been given access.
If the users have also been granted global Read permission on Certificates, they can modify the metadata of any certificates within the Keyfactor Command database. If the users have not been granted the global Read permission, they can only modify the certificates found in collections to which they have been granted collection-level Read access.
Users with the Import role permission for Certificates can use the Add Certificate option under the Certificate Locations menu (see Add Certificate). This is a global role only and not set on a collection-by-collection basis.
Users with the Download with Private Key role permission for Certificates will need to also have their security permissions set to Include Private Key![]() Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. option (see Security Role Permissions) to allow the users to download the private key of a certificate on any certificates to which they have been granted access if it is stored in the Keyfactor Command database or recoverable using Microsoft key recovery.
Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. option (see Security Role Permissions) to allow the users to download the private key of a certificate on any certificates to which they have been granted access if it is stored in the Keyfactor Command database or recoverable using Microsoft key recovery.
Users with the Revoke role permission for Certificates can use the revoke certificate operation on any certificates to which they have been granted access. This includes certificates that have been issued by a local Microsoft CA![]() A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. or by a cloud-based certificate vendor that is managed via a Keyfactor certificate gateway.
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. or by a cloud-based certificate vendor that is managed via a Keyfactor certificate gateway.
Users with the Delete role permission for Certificates can delete certificates and private keys from the Keyfactor Command database.
Users with the Import Private Key role permission for Certificates can add a certificate with an associated private key through the Add Certificate option under the Certificate Locations menu (see Add Certificate) and the private key will be stored in the Keyfactor Command database. Users must also be granted the Import role in order to be able to use the Add Certificate feature. This is a global role only and not set on a collection-by-collection basis.

