Register a Client Certificate Renewal Extension
The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator![]() The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to interact with Windows servers (a.k.a. IIS certificate stores) and FTP capable devices for certificate management, run SSL discovery and management tasks, and manage synchronization of certificate authorities in remote forests. With the addition of custom extensions, it can run custom jobs to provide certificate management capabilities on a variety of platforms and devices (e.g. F5 devices, NetScaler devices, Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources) and execute tasks outside the standard list of certificate management functions. It runs on either Windows or Linux. supports automated renewal of the certificate used for client certificate authentication. It does this using a custom extension point interface on the orchestrator
The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to interact with Windows servers (a.k.a. IIS certificate stores) and FTP capable devices for certificate management, run SSL discovery and management tasks, and manage synchronization of certificate authorities in remote forests. With the addition of custom extensions, it can run custom jobs to provide certificate management capabilities on a variety of platforms and devices (e.g. F5 devices, NetScaler devices, Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources) and execute tasks outside the standard list of certificate management functions. It runs on either Windows or Linux. supports automated renewal of the certificate used for client certificate authentication. It does this using a custom extension point interface on the orchestrator![]() Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. that can be implemented by the end user. When the client certificate used for authentication by the orchestrator is approaching expiration (within 180 days of expiration by default), the extension generates a CSR
Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. that can be implemented by the end user. When the client certificate used for authentication by the orchestrator is approaching expiration (within 180 days of expiration by default), the extension generates a CSR![]() A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. with a private key
A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. with a private key![]() Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. and submits the CSR to Keyfactor Command for enrollment
Private keys are used in cryptography (symmetric and asymmetric) to encrypt or sign content. In asymmetric cryptography, they are used together in a key pair with a public key. The private or secret key is retained by the key's creator, making it highly secure. and submits the CSR to Keyfactor Command for enrollment![]() Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA).. When Keyfactor Command returns the certificate to the orchestrator, it is paired with the private key and installed for use as the client certificate for authentication. The extension both supplies the information for the CSR and holds a dictionary of client parameters (see Build a Client Certificate Renewal Extension).
Certificate enrollment refers to the process by which a user requests a digital certificate. The user must submit the request to a certificate authority (CA).. When Keyfactor Command returns the certificate to the orchestrator, it is paired with the private key and installed for use as the client certificate for authentication. The extension both supplies the information for the CSR and holds a dictionary of client parameters (see Build a Client Certificate Renewal Extension).
To register a client authentication certificate renewal extension:
- Create the extension DLL (see Build a Client Certificate Renewal Extension).
-
On the Universal Orchestrator server, locate the extensions folder under the install directory for the orchestrator. By default, this is:
Windows: C:\Program Files\Keyfactor\Keyfactor Orchestrator\extensions
Linux: /opt/keyfactor/orchestrator/extensions - Under the extensions directory, create a new directory for your extension (e.g. CertRotation).
- Place your DLL in the new CertRotation directory.
- Create a manifest.json file in the CertRotation directory with the following contents:
{ "extensions": { "Keyfactor.Orchestrators.Extensions.IOrchestratorRegistrationUpdater": { "RegisteredRegistrationUpdater": { "assemblypath": "RegistrationUpdater.dll", "TypeFullName": "Custom.Registration.Updaters.CustomRegistrationUpdater", "config": { "DnsSan": "orchestrator_name.keyexample.com", "Subject": "CN=Client Certificate Authentication", "DataCenter": "WestCoast", "ForceRenewal": "False" } } } } }Only the values shown in red above should be modified from what is shown in this example:
The assemblypath is the name of your DLL.
The example Custom.Registration.Updaters portion of the TypeFullName must match the namespace in your code. The example CustomRegistrationUpdater portion of the TypeFullName must match the class in your code.
The config section is only needed if you wish to pass configuration values such as a standard DNS
 The Domain Name System is a service that translates names into IP addresses. SAN
The Domain Name System is a service that translates names into IP addresses. SAN The subject alternative name (SAN) is an extension to the X.509 specification that allows you to specify additional values when enrolling for a digital certificate. A variety of SAN formats are supported, with DNS name being the most common. or certificate subject into the extension. Those shown here are examples that match the sample code (see Build a Client Certificate Renewal Extension).
The subject alternative name (SAN) is an extension to the X.509 specification that allows you to specify additional values when enrolling for a digital certificate. A variety of SAN formats are supported, with DNS name being the most common. or certificate subject into the extension. Those shown here are examples that match the sample code (see Build a Client Certificate Renewal Extension).
The certificate renewal process occurs as follows:
- When each registration or session renewal of the orchestrator service occurs, the orchestrator, in conjunction with underlying Keyfactor Command functionality, checks the expiration date of the client authentication certificate and compares that with the defined client certificate warning period (180 days) and expiry period (30 days) in Keyfactor Command to determine whether a new certificate is needed.
Note: If the certificate is in the warning period, operations will continue while a new certificate is requested. If the certificate is in the expiry period or already expired, the orchestrator will not be allowed to register a new session when the existing session expires or the orchestrator service is restarted.
Orchestrator log messages indicating that a certificate is in the warning period look similar to the following:
2021-09-17 12:45:59.7927 Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobEngine.SessionClient [Warn] - Remote CMS call 'https://keyfactor.keyexample.com/KeyfactorAgents/Session/Register' returned: Agent certificate is approaching expiration and should be renewed. (A0100007)
Orchestrator log messages indicating that a certificate is in the expiry period look similar to the following:
2021-09-09 17:27:37.5367 Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobEngine.SessionClient [Error] - Remote CMS call 'https://keyfactor.keyexample.com/KeyfactorAgents/Session/Register' returned: Agent certificate is approaching expiration and must be renewed. (A0100008) 2021-09-09 17:27:37.5642 Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobEngine.SessionJobExecutor [Error] - Error in SessionManager: Unable to register session. at Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobEngine.SessionClient.RegisterAsync(IEnumerable`1 capabilities, CancellationToken cancellationToken) at Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobEngine.SessionJobExecutor.Execute(IJobExecutionContext context)
Error: A0100008 Agent certificate is approaching expiration and must be renewed. at Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobEngine.SessionClient.RegisterAsync(IEnumerable`1 capabilities, CancellationToken cancellationToken)Tip: The length of the warning period and expiry period are defined in Keyfactor Command and are not user-configurable values. Contact support@keyfactor.com if you need to modify these values.Tip: The orchestrator can be forced into the warning or expiry state before it reaches these based on certificate lifetime using the POST /Agents/SetAuthCertificateReenrollment method in the Keyfactor API A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. or the Request Renewal button on the Orchestrator Management page of the Keyfactor Command Management Portal. A status of Request (1) is the equivalent of the warning period and a status of Require (2) is the equivalent of the expiry period.
A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. or the Request Renewal button on the Orchestrator Management page of the Keyfactor Command Management Portal. A status of Request (1) is the equivalent of the warning period and a status of Require (2) is the equivalent of the expiry period. -
When either the warning period or expiry period is identified, the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator will pass a value of true to the GetCSRInfo method (newOrchestratorCertRequestedByPlatform in the sample extension—see Build a Client Certificate Renewal Extension). The extension generates a private key and a CSR using CSR information (e.g. subject, key size
 The key size or key length is the number of bits in a key used by a cryptographic algorithm.) provided or generated by the extension (depending on the extension design), returns the CSR to the orchestrator, which submits it to Keyfactor Command for certificate enrollment.
The key size or key length is the number of bits in a key used by a cryptographic algorithm.) provided or generated by the extension (depending on the extension design), returns the CSR to the orchestrator, which submits it to Keyfactor Command for certificate enrollment.If the certificate is within the warning period but not within the expiry period, orchestrator activity will be allowed to continue as usual. If the certificate is within the expiry period, a new session will not be granted when the orchestrator requests a new session and orchestrator activity will not be allowed to continue until the orchestrator acquires a new certificate. If the certificate has expired, the certificate rotation cannot take place since the orchestrator cannot authenticate to Keyfactor Command to complete the rotation.
Tip: If a certificate has expired or some other certificate problem is causing the orchestrator not to be able to acquire a session, the orchestrator can be reset using either the Reset button on the Orchestrator Management page in the Keyfactor Command Management Portal or the POST /Agents/{id}/Reset method in the Keyfactor API. This removes the certificate history and allows the orchestrator to register for a session with the certificate currently configured in the appsettings.json file under the configuration directory. You will need to re-approve the orchestrator if you reset it. -
In Keyfactor Command, a certificate is issued based on:
- The OrchestratorConstants.CertificateAttributes.CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY and OrchestratorConstants.CertificateAttributes.CERTIFICATE_TEMPLATE
 A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. values defined in the custom registration handler enroll function.
A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. values defined in the custom registration handler enroll function. - If no values are supplied in the custom registration handler enroll function, the certificate authority
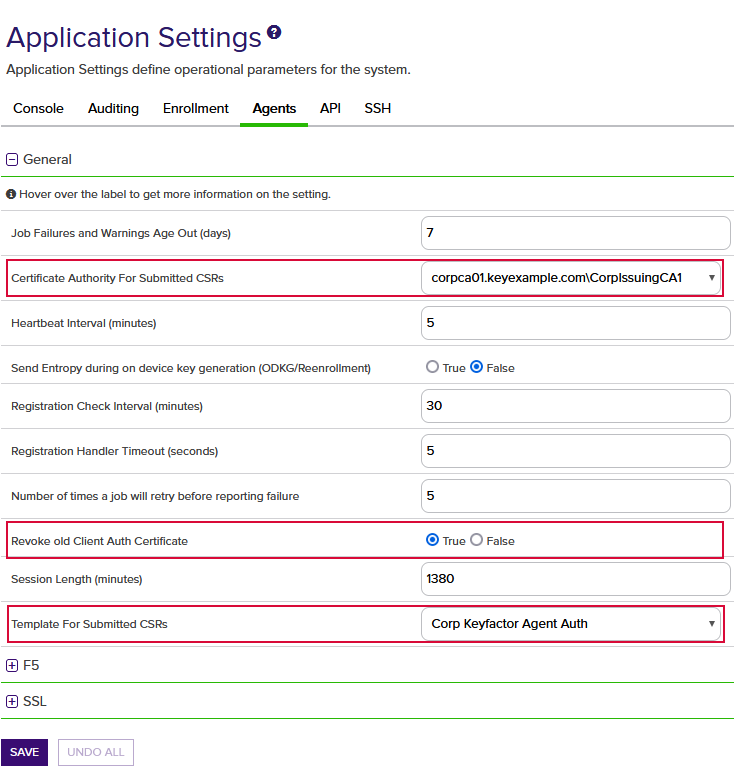
 A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. and template defined by the Certificate Authority For Submitted CSRs and Template For Submitted CSRs application settings in the Keyfactor Command Management Portal.
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. and template defined by the Certificate Authority For Submitted CSRs and Template For Submitted CSRs application settings in the Keyfactor Command Management Portal.
- The OrchestratorConstants.CertificateAttributes.CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY and OrchestratorConstants.CertificateAttributes.CERTIFICATE_TEMPLATE
- Once the certificate is issued, it is returned to the orchestrator and married with the private key. If certificate authentication is configured using a certificate stored in the local computer or Universal Orchestrator service account user's personal store (Windows only), the orchestrator updates the appsettings.json file with the thumbprint of the new certificate. The thumbprint is stored in the AuthCertThumbprint value in the appsettings.json file (see Change Service Account Passwords). If certificate authentication is configured using a PKCS12 file stored in the file system, a PKCS12 file is generated and replaces the original PKCS12 file. The randomly generated password for the PKCS12 file is updated in the orchestratorsecrets.json file.
Note: If certificate authentication is configured using a certificate stored in the local computer personal store on Windows, when the new certificate is generated, it will be placed in the service account user's personal store, not the local computer personal store. This is true if the service is running as a domain account and if the service is running as the default Network Service.
- With the orchestrator's next session registration or heartbeat, it will begin using the new certificate.Tip: If you manually configured the orchestrator to renew the certificate using the POST /Agents/SetAuthCertificateReenrollment method in the Keyfactor API or the Request Renewal button on the Orchestrator Management page, that flag will be cleared when the orchestrator successfully registers for a session or completes a heartbeat using the new certificate.
Once a new session is established with the new certificate, the stored legacy thumbprint for the replaced certificate will be removed from the database. This occurs whether or not you opt to automatically revoke the old certificate and occurs before the certificate revocation takes place. The legacy thumbprint is not cleared on a heartbeat with the new certificate.
- If you've opted to enable the Revoke old Client Auth Certificate application setting (see Figure 538: Application Settings for Client Certificate Renewal) in Keyfactor Command, the previous certificate for the orchestrator will be revoked automatically by Keyfactor Command once the orchestrator has made a successful registered for a new session with the new certificate.Important: The Universal Orchestrator service account under which the orchestrator is operating must have permissions to enroll for certificates from the CA
 A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. and have at least the Enroll CSR role permission for Certificate Enrollment and the Read role permission for Certificates in Keyfactor Command. If you've opted to enable automated revocation of the old certificate, the service account must also have permissions to revoke certificates on the CA and have at least the Revoke role permission for Certificates in Keyfactor Command.
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. and have at least the Enroll CSR role permission for Certificate Enrollment and the Read role permission for Certificates in Keyfactor Command. If you've opted to enable automated revocation of the old certificate, the service account must also have permissions to revoke certificates on the CA and have at least the Revoke role permission for Certificates in Keyfactor Command.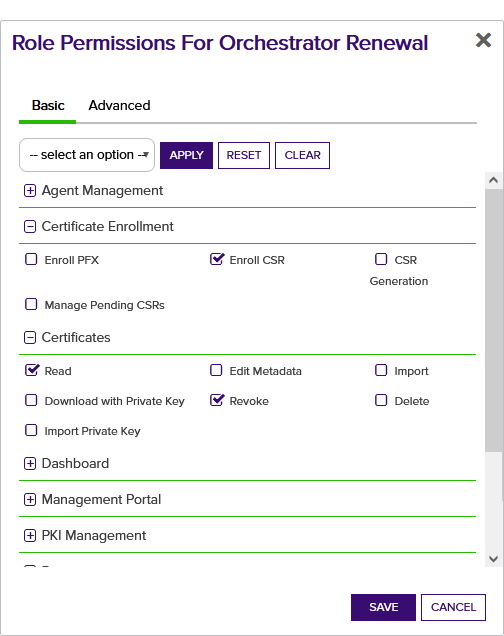
Figure 539: Keyfactor Command Permissions Required for Automatic Renewal and Revocation of Client Authentication Certificates