The PKI![]() A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. Status for Collection
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. Status for Collection![]() The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports). report is a multi-page report incorporating tables and charts that provides an overview of the status of the certificates in the selected collection.
The certificate search function allows you to query the Keyfactor Command database for certificates from any available source based on any criteria of the certificates and save the results as a collection that will be availble in other places in the Management Portal (e.g. expiration alerts and certain reports). report is a multi-page report incorporating tables and charts that provides an overview of the status of the certificates in the selected collection.

Figure 85: PKI Status for Collection Summary
The export options for the PKI Status for Collection report are Excel and PDF.
This report takes as an input parameter![]() A parameter or argument is a value that is passed into a function in an application.
A parameter or argument is a value that is passed into a function in an application.
-
Certificate Collection: Select the certificate collection using the search select list, which includes the built-in option, All Certificates collection. and has the option to include or exclude certificates that have a status of unknown (certificates found on SSL
 TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. scans and in certificate stores often have this status - unknown certificates are excluded by default). To narrow the list of results in the search select field, begin typing a search string in the search field.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) are protocols for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. scans and in certificate stores often have this status - unknown certificates are excluded by default). To narrow the list of results in the search select field, begin typing a search string in the search field.
Sections of the report include:
 Summary Page
Summary Page
The summary page provides certificate counts for the following:
-
Total number of active certificates
This value excludes expired and revoked certificates and only includes non-expired, non-revoked certificates with an unknown state if the Include Unknown checkbox is selected at runtime.
- Number of certificates issued in the most recently completed week, beginning with a Sunday
- Number of expired certificates
- Number of certificates coming up for expiration within two weeks
- Number of certificates coming up for expiration within two months (including those expiring within two weeks)
- Number of certificates coming up for expiration within six months (including those expiring within two weeks and two months)
- A breakdown of the number of active certificates by signing algorithm (only the top five signing algorithms are shown)
- The top five issuers of active certificates with the number of active certificates
 Next Ten Certificates to Expire Page
Next Ten Certificates to Expire Page
This table shows details of the ten certificates expiring within the shortest timeframe (for any timeframe under two years) and includes the certificate CN![]() A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com)., issuer CN, certificate validity period in UTC time, template
A common name (CN) is the component of a distinguished name (DN) that represents the primary name of the object. The value varies depending on the type of object. For a user object, this would be the user's name (e.g. CN=John Smith). For SSL certificates, the CN is typically the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host where the SSL certificate will reside (e.g. servername.keyexample.com or www.keyexample.com)., issuer CN, certificate validity period in UTC time, template![]() A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. name, thumbprint and serial number. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (
A certificate template defines the policies and rules that a CA uses when a request for a certificate is received. name, thumbprint and serial number. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
 PKI Health Metrics—Lifetime Remaining Page
PKI Health Metrics—Lifetime Remaining Page
This donut chart shows the percentage of certificates that are expired, near expiration (90% or more of lifetime used) or active and not near expiration along with a table showing the specific numbers in these categories. Hover over a segment in the donut chart to see details for that segment. Click one of the labels below the donut chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
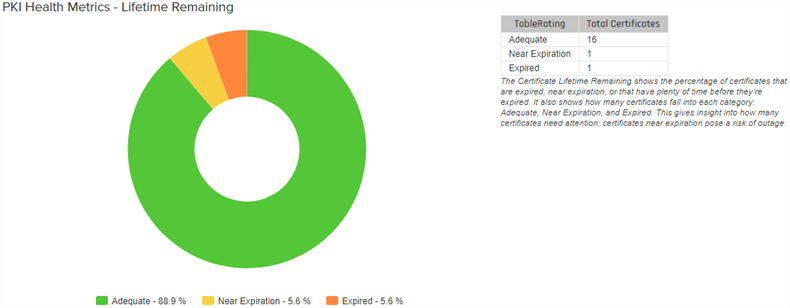
Figure 86: PKI Status for Collection Lifetime Remaining
 PKI Health Metrics—Algorithm Strength
PKI Health Metrics—Algorithm Strength
This donut chart shows the percentage of certificates (active and expired) with strong (SHA2 and SSA), weak (SHA1) or critically weak (MD5 and older) signature algorithms along with a table showing the specific numbers in these categories. Hover over a segment in the donut chart to see details for that segment. Click one of the labels below the donut chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
 PKI Health Metrics—RSA Key Strength
PKI Health Metrics—RSA Key Strength
This donut chart shows the percentage of certificates (active and expired) with strong (2048+), weak (1024-2047), and critically weak (<1024) RSA keys along with a table showing the specific numbers in these categories. Hover over a segment in the donut chart to see details for that segment. Click one of the labels below the donut chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
 Certificates by Signing Algorithm
Certificates by Signing Algorithm
This donut chart shows the percentage of active certificates broken down by signing algorithm (RSA SHA-1, RSA SHA-256, etc.) along with a table showing the specific numbers in these categories. Hover over a segment in the donut chart to see details for that segment. Click one of the labels below the donut chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart.
 Top Certificate Issuers
Top Certificate Issuers
This donut chart shows the percentage of certificates (active and expired) broken down by the top five issuers plus an other bucket along with a table showing the specific numbers in these categories. Hover over a segment in the donut chart to see details for that segment. Click one of the labels below the donut chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
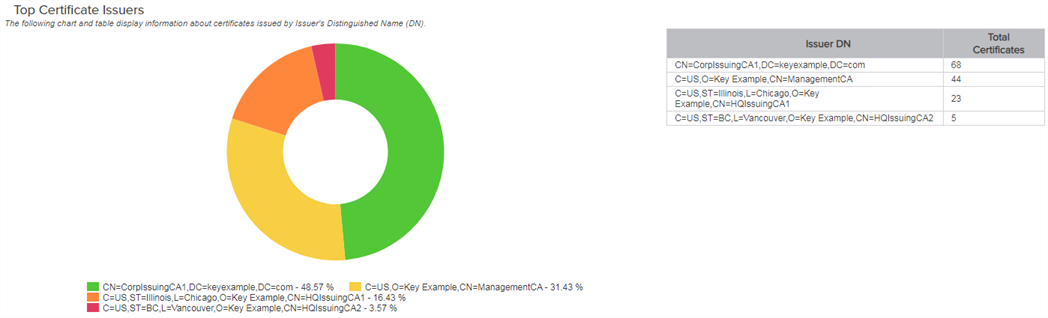
Figure 87: PKI Status for Collection Top Issuers
 Certificates Issued in Previous 10 Weeks
Certificates Issued in Previous 10 Weeks
This bar chart shows the number of certificates (active and expired) issued per week for the ten weeks leading up to and through the full week prior to the run date of the report. Hover over a bar to see the number of issued certificates for the week with that date.
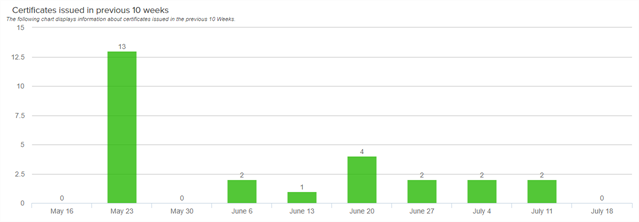
Figure 88: PKI Status for Certificates issued in previous 10 weeks
 Certificates Issued in Previous 12 Months
Certificates Issued in Previous 12 Months
This bar chart shows the number of certificates (active and expired) issued per month for the twelve months leading up to and through the full month prior to the run date of the report, broken down by internally issued certificates (from sources managed by Keyfactor Command such as synchronization of CAs in the primary forest![]() An Active Directory forest (AD forest) is the top most logical container in an Active Directory configuration that contains domains, and objects such as users and computers. and any trusted forests, any certificate vendors synced using a Keyfactor gateway, and any CAs synced using the remote CA
An Active Directory forest (AD forest) is the top most logical container in an Active Directory configuration that contains domains, and objects such as users and computers. and any trusted forests, any certificate vendors synced using a Keyfactor gateway, and any CAs synced using the remote CA![]() A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. agent) and externally issued certificates (from sources not managed by Keyfactor Command such as certificates located during SSL scans or uploaded using the Add Certificate option). Hover over a bar to see the number of issued certificates for that month and source. Click one of the labels below the chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart.
A certificate authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. Within Keyfactor Command, a CA may be a Microsoft CA or a Keyfactor gateway to a cloud-based or remote CA. agent) and externally issued certificates (from sources not managed by Keyfactor Command such as certificates located during SSL scans or uploaded using the Add Certificate option). Hover over a bar to see the number of issued certificates for that month and source. Click one of the labels below the chart to toggle add/remove the segment on the chart.
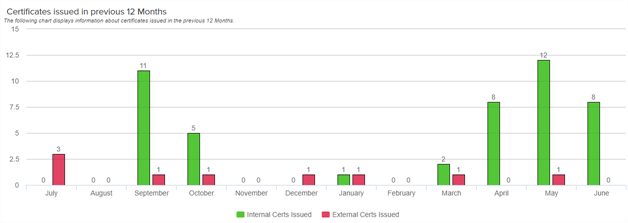
Figure 89: PKI Status for Certificates issued in previous 12 months
 Weak RSA Certificates
Weak RSA Certificates
This table shows details of the certificates with weak (under 2048) RSA keys and includes the certificate CN, issuer CN, certificate validity period in UTC time, key size![]() The key size or key length is the number of bits in a key used by a cryptographic algorithm., thumbprint and serial number. A maximum of 1000 certificates is shown. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (
The key size or key length is the number of bits in a key used by a cryptographic algorithm., thumbprint and serial number. A maximum of 1000 certificates is shown. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
 Deprecated Signing Algorithms
Deprecated Signing Algorithms
This table shows details of the certificates with deprecated (MD5 and older) signing algorithms and includes the certificate CN, issuer CN, certificate validity period in UTC time, signing algorithm, thumbprint and serial number. A maximum of 1000 certificates is shown. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
 Self-Signed Certificates
Self-Signed Certificates
This table shows details of the certificates that are self-signed or root CA certificates and includes the certificate DN![]() A distinguished name (DN) is the name that uniquely identifies an object in a directory. In the context of Keyfactor Command, this directory is generally Active Directory. A DN is made up of attribute=value pairs, separated by commas. Any of the attributes defined in the directory schema can be used to make up a DN., certificate validity period in UTC time, thumbprint and serial number. A maximum of 1000 certificates is shown. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (
A distinguished name (DN) is the name that uniquely identifies an object in a directory. In the context of Keyfactor Command, this directory is generally Active Directory. A DN is made up of attribute=value pairs, separated by commas. Any of the attributes defined in the directory schema can be used to make up a DN., certificate validity period in UTC time, thumbprint and serial number. A maximum of 1000 certificates is shown. Grid columns may be rearranged by click-holding and dragging the grid arrangement control icon (![]() ) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
) at the left of the column header. Click a column header to sort the grid by ascending values; click again to sort descending (columns already in ascending order will switch to descending on the first click). The screen will redraw when you sort. Not all columns are sortable.
Was this page helpful? Provide Feedback