To select a single row in the orchestrator![]() Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. management grid, click to highlight it and then select an operation from either the top of the grid or the right-click menu. The approve, disapprove, apply blueprint
Keyfactor orchestrators perform a variety of functions, including managing certificate stores and SSH key stores. management grid, click to highlight it and then select an operation from either the top of the grid or the right-click menu. The approve, disapprove, apply blueprint![]() A snapshot of the certificate stores and scheduled jobs on one orchestrator, which can be used to create matching certificate stores and jobs on another orchestrator with just a few clicks., reset, and request renewal operations can be done on multiple orchestrators at once. To select multiple rows, click the checkbox for each row on which you would like to perform an operation. Then select an operation from the top of the grid. The right-click menu supports operations on only one orchestrator at a time.
A snapshot of the certificate stores and scheduled jobs on one orchestrator, which can be used to create matching certificate stores and jobs on another orchestrator with just a few clicks., reset, and request renewal operations can be done on multiple orchestrators at once. To select multiple rows, click the checkbox for each row on which you would like to perform an operation. Then select an operation from the top of the grid. The right-click menu supports operations on only one orchestrator at a time.
 Viewing Orchestrator Details
Viewing Orchestrator Details
To view details of an orchestrator, double-click the orchestrator, right-click the orchestrator and choose View Details from the right-click menu, or highlight the row in the grid and click View Details at the top of the grid. The orchestrator details dialog includes this information:
Details Tab
The GUID of the orchestrator.
The host name![]() The unique identifier that serves as name of a computer. It is sometimes presented as a fully qualified domain name (e.g. servername.keyexample.com) and sometimes just as a short name (e.g. servername). of the orchestrator machine, either short or fully qualified depending upon how the machine reports itself.
The unique identifier that serves as name of a computer. It is sometimes presented as a fully qualified domain name (e.g. servername.keyexample.com) and sometimes just as a short name (e.g. servername). of the orchestrator machine, either short or fully qualified depending upon how the machine reports itself.
The account the orchestrator is using to authenticate to Keyfactor Command, which may or may not be the same as the account under which the orchestrator is running. For example, the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator![]() The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to interact with servers and devices for certificate management, run SSL discovery and management tasks, and manage synchronization of certificate authorities in remote forests. With the addition of custom extensions, it can provide certificate management capabilities on a variety of platforms and devices (e.g. Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources, Citrix\NetScaler devices, F5 devices, IIS stores, JKS keystores, PEM stores, and PKCS#12 stores) and execute tasks outside the standard list of certificate management functions. It runs on either Windows or Linux servers or Linux containers. service runs as a service account on the orchestrator machine that may be a local account on the machine, the Windows built-in Network Service account, or an Active Directory domain account. If it’s an Active Directory account, it will be an account in the forest
The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to interact with servers and devices for certificate management, run SSL discovery and management tasks, and manage synchronization of certificate authorities in remote forests. With the addition of custom extensions, it can provide certificate management capabilities on a variety of platforms and devices (e.g. Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources, Citrix\NetScaler devices, F5 devices, IIS stores, JKS keystores, PEM stores, and PKCS#12 stores) and execute tasks outside the standard list of certificate management functions. It runs on either Windows or Linux servers or Linux containers. service runs as a service account on the orchestrator machine that may be a local account on the machine, the Windows built-in Network Service account, or an Active Directory domain account. If it’s an Active Directory account, it will be an account in the forest![]() An Active Directory forest (AD forest) is the top most logical container in an Active Directory configuration that contains domains, and objects such as users and computers. to which the orchestrator server is joined. The orchestrator’s identity to make the connection to the Keyfactor Command server will be a service account for the identity provider configured for Keyfactor Command, which may be Active Directory, Keyfactor Identity Provider, Auth0, another OAuth 2.0 complient identity provider, or a federated identity provider. If it’s Active Directory, it will be an identity from the forest in which Keyfactor Command is installed, which may be a different forest from the forest in which the orchestrator is installed.
An Active Directory forest (AD forest) is the top most logical container in an Active Directory configuration that contains domains, and objects such as users and computers. to which the orchestrator server is joined. The orchestrator’s identity to make the connection to the Keyfactor Command server will be a service account for the identity provider configured for Keyfactor Command, which may be Active Directory, Keyfactor Identity Provider, Auth0, another OAuth 2.0 complient identity provider, or a federated identity provider. If it’s Active Directory, it will be an identity from the forest in which Keyfactor Command is installed, which may be a different forest from the forest in which the orchestrator is installed.
The platform of the orchestrator—Java for the Java Agent![]() The Java Agent, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to perform discovery of Java keystores and PEM certificate stores, to inventory discovered stores, and to push certificates out to stores as needed., .NET Core for the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, Bash for the Keyfactor Bash Orchestrator
The Java Agent, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to perform discovery of Java keystores and PEM certificate stores, to inventory discovered stores, and to push certificates out to stores as needed., .NET Core for the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, Bash for the Keyfactor Bash Orchestrator![]() The Bash Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to discover and manage SSH keys across an enterprise., for example.
The Bash Orchestrator, one of Keyfactor's suite of orchestrators, is used to discover and manage SSH keys across an enterprise., for example.
The version number that the orchestrator has reported.
Whether the orchestrator has been approved for operations with the Keyfactor Command server. Newly registered orchestrators show New in this column. Disapproved orchestrators show Disapproved.
The date and time when the orchestrator last contacted the Keyfactor Command server.
The target capabilities that are supported by that orchestrator as appropriate for the type of orchestrator. This includes custom capabilities.
The last blueprint applied to the orchestrator, if any (see Orchestrator Blueprints).
The thumbprint of the certificate previously used by the orchestrator for client certificate authentication before a certificate renewal operation took place (rotating the current thumbprint into the legacy thumbprint). The legacy thumbprint is cleared once the orchestrator successfully registers with a new thumbprint.
The thumbprint of the certificate that Keyfactor Command is expecting the orchestrator to use for client certificate authentication.
The last error code, if any, reported from the orchestrator when trying to register a session. This code is cleared on successful session registration.
The thumbprint of the certificate that the orchestrator most recently used for client certificate authentication. In most cases, this will match the Current Thumbprint.
The last error code, if any, reported from the orchestrator when trying to register a session. This code is cleared on successful session registration.
The last error code, if any, reported from the orchestrator when trying to register a session. This message is cleared on successful session registration.
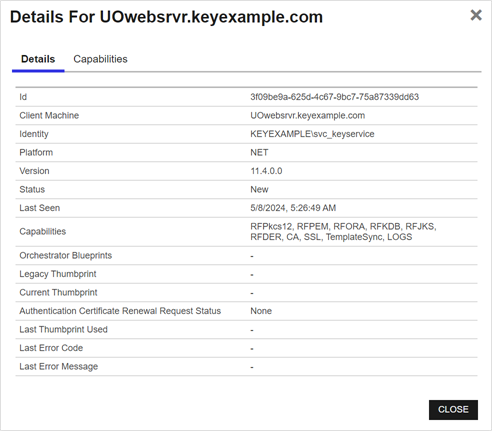
Figure 297: View Details for an Orchestrator
Capabilities Tab
The Capability tab shows a list of JobTypes that are correlated to the selected orchestrator's capabilities. For Custom job types only the Name will display (Short Name and Cert Store Job Type will be blank).
The name of the job type which includes each combination of capability and the job type.
The user-defined short name given to the certificate store associated with the job type.
The job type:
- Inventory: Determine what is in the certificate store(s) and report the contents to Keyfactor Command. This capability is required for all store types.
- Add: Add new certificates to a certificate store.
- Remove: Remove certificates from a certificate store.
- Create: Create a new certificate store.
- Discovery: Determine what certificate stores of this type are on the device.
- Reenrollment: Generate a keypair on the device and submit a certificate signing request
 A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. using on-device key generation (ODKG).
A CSR or certificate signing request is a block of encoded text that is submitted to a CA when enrolling for a certificate. When you generate a CSR within Keyfactor Command, the matching private key for it is stored in Keyfactor Command in encrypted format and will be married with the certificate once returned from the CA. using on-device key generation (ODKG).
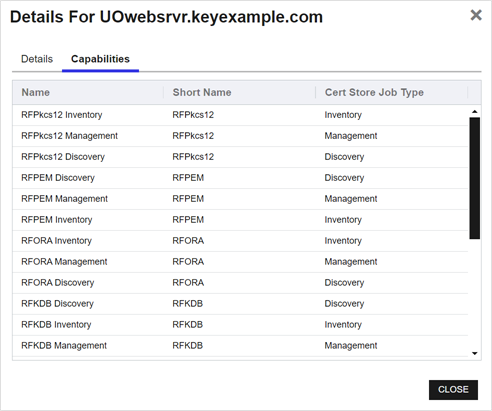
Figure 298: View Details for an Orchestrator
 Approving or Disapproving Orchestrators
Approving or Disapproving Orchestrators
When orchestrators first appear in Keyfactor Command, they have a status of New. The orchestrator cannot perform any jobs while it has this status. To approve an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Approve at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose Approve from the right-click menu. Once you have approved a Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator or Keyfactor Java Agent, you can schedule jobs for the orchestrator. Once you have approved an SSH![]() The SSH (secure shell) protocol provides for secure connections between computers. It provides several options for authentication, including public key, and protects the communications with strong encryption. Orchestrator, you can configure server groups and servers for that orchestrator and begin scanning servers.
The SSH (secure shell) protocol provides for secure connections between computers. It provides several options for authentication, including public key, and protects the communications with strong encryption. Orchestrator, you can configure server groups and servers for that orchestrator and begin scanning servers.
To disapprove an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Disapprove at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose Disapprove from the right-click menu. When an orchestrator is disapproved, operations with Keyfactor Command can no longer be carried out by this orchestrator.
 Generating and Applying Blueprints
Generating and Applying Blueprints
To generate a blueprint from an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Generate Blueprint at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose Generate Blueprint from the right-click menu. For more information about blueprints, see Orchestrator Blueprints.
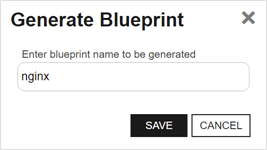
Figure 299: Generate a Blueprint from an Existing Orchestrator
To apply a blueprint to an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Apply Blueprint at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose Apply Blueprint from the right-click menu. For more information about blueprints, see Orchestrator Blueprints.
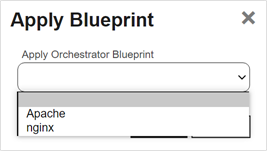
Figure 300: Apply a Blueprint from a New Orchestrator
 Orchestrator Reset
Orchestrator Reset
The orchestrator reset and renewal functions are both useful for orchestrator maintenance. The reset function can be used when an orchestrator is in an error state or if you've made some changes on the orchestrator side that necessitate a refresh. The orchestrator reset function:
- Removes all current orchestrator jobs for the selected orchestrator.
- Deletes all associated certificate stores.
- Sets the orchestrator status to new.
- For orchestrators configured to use client certificate authentication, clears the certificate thumbprints stored for the orchestrator to allow it to be reconfigured with a new certificate.
To reset an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Reset at the top of the grid or right-click the agent in the grid and choose Reset from the right-click menu.
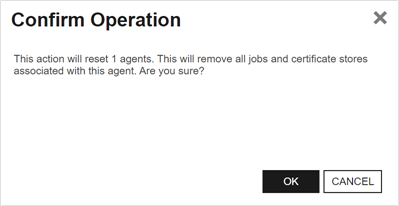
Figure 301: Reset an Orchestrator
 Orchestrator Renewal
Orchestrator Renewal
The renewal function is used for orchestrators that are authenticating via client certificate to initiate a client certificate renewal before this would occur automatically based on approaching certificate expiration. The renewal function requests or requires that the orchestrator enroll for a new client authentication certificate on the orchestrator's next session registration. It is used in conjunction with a custom renewal extension on the orchestrator to force the orchestrator to enroll for a new certificate before it would normally do so based on the warning and expiry windows. See Register a Client Certificate Renewal Extension for more information and custom renewal extensions on the renewal process.
To request certificate renewal for an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Request Renewal at the top of the grid or right-click the agent in the grid and choose Request Renewal from the right-click menu. In the Renewal Status dropdown, select one of the available options:
-
None
Unset the value so that the orchestrator will not request a new client authentication certificate (based on this value). -
Request
The orchestrator will request a new client authentication certificate when it next registers for a session. Orchestrator activity will be allowed to continue as usual. -
Require
The orchestrator will request a new client authentication certificate when it next registers for a session. A new session will not be granted and orchestrator activity will not be allowed to continue until the orchestrator acquires a new certificate.

Figure 302: Request Renewal for an Orchestrator
 Viewing Active Jobs for an Orchestrator
Viewing Active Jobs for an Orchestrator
To view all the active jobs for an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click View Jobs at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose View Jobs from the right-click menu. This will take you to the scheduled jobs tab of the orchestrator job status page with the query field populated by the selected orchestrator.
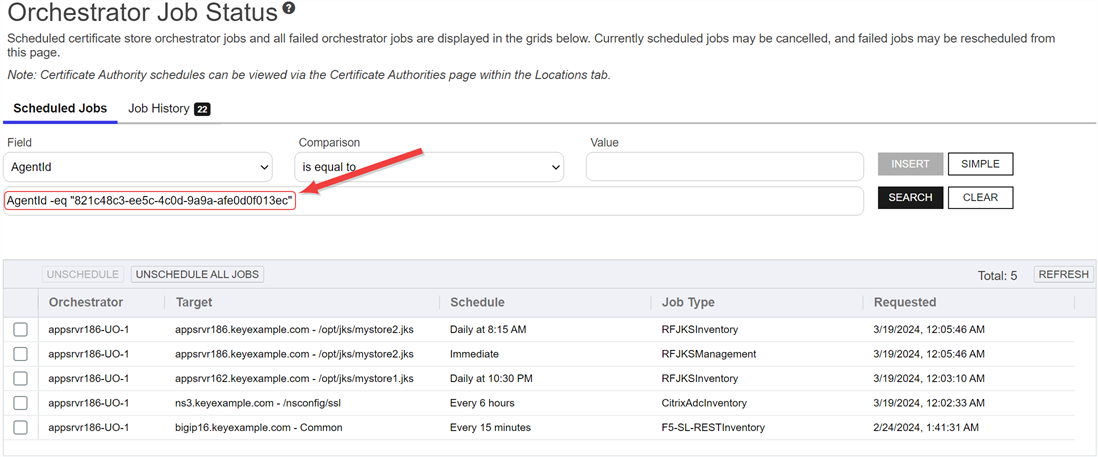
Figure 303: View Active Jobs for an Orchestrator
 Viewing the Job History for an Orchestrator
Viewing the Job History for an Orchestrator
To view job history for an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click View Job Histories at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose View Job Histories from the right-click menu. This will take you to the job history tab of the orchestrator job status page with the query field populated by the selected orchestrator.
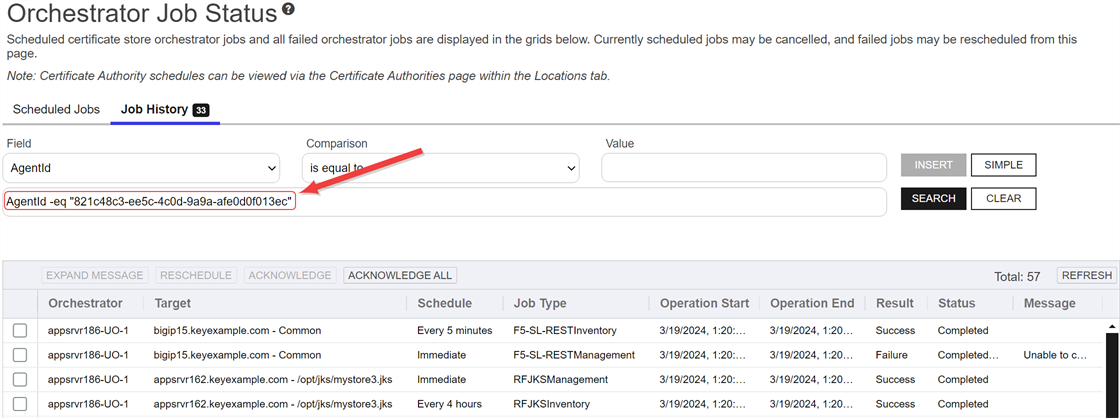
Figure 304: View Job History for an Orchestrator
 Viewing Certificate Stores Associated with an Orchestrator
Viewing Certificate Stores Associated with an Orchestrator
To view the certificate stores associated with an orchestrator, highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click View Certificate Stores at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose View Certificate Stores from the right-click menu. This will take you to the certificate stores page with the query field populated by the selected orchestrator.
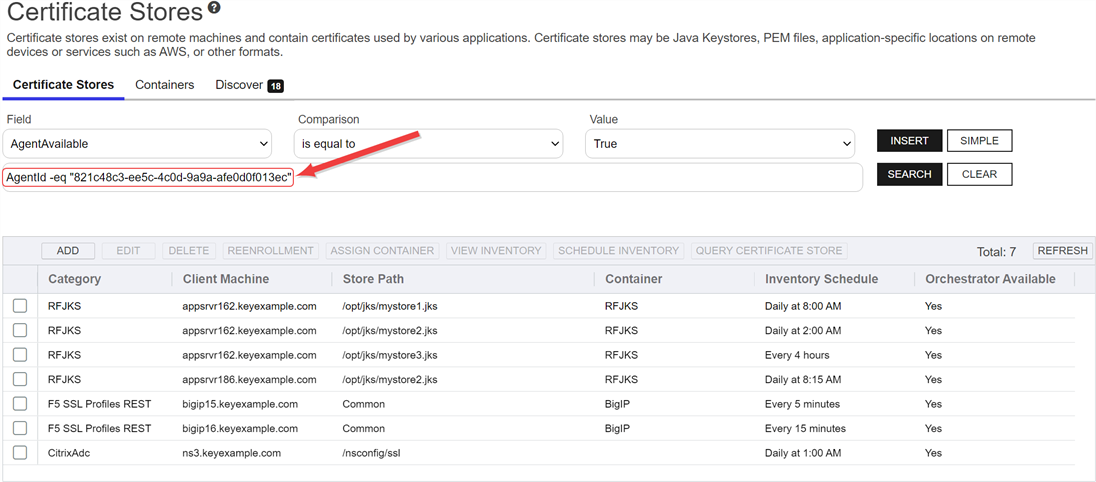
Figure 305: View Certificate Stores for an Orchestrator
 Fetch Logs
Fetch Logs
The fetch logs function is designed to retrieve a portion of the tail end of the orchestrator log for easy review. It is supported for both the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator and the Native Agent.
To schedule a job to fetch the logs, click Fetch Logs from the actions buttons at the top of the Orchestrator Management grid or from the right-click menu. The job will be scheduled to run immediately, which means it should complete within a few minutes depending on other activity occurring at the same time. The fetch logs job will appear in Scheduled Jobs under Orchestrator Job Status with a job type of Fetch Logs and when complete will appear in Job History (see Job History).
For Native Agent fetch log jobs, when the job is complete, locate the completed job on the Job History tab and double-click or click Expand Message from the right-click menu or at the top of the grid. The job status message details show 4000 characters of the tail end of the log.
To review the log data for logs fetched from a Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator, use the GET /OrchestratorJobs/JobStatus/Data Keyfactor API![]() A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. method. See GET Orchestrator Jobs Job Status Data for more information.
A set of functions to allow creation of applications. Keyfactor offers the Keyfactor API, which allows third-party software to integrate with the advanced certificate enrollment and management features of Keyfactor Command. method. See GET Orchestrator Jobs Job Status Data for more information.
To set up logging on the Native Agent, see the Native Agent configuration instructions to configure logging and start the orchestrator with the appropriate logging level to allow for the use of the Fetch Logs feature:
2021-08-05 10:47:23.1940 Keyfactor.Orchestrators.JobExecutors.OrchestratorJobExecutor [Debug] - Response status code does not indicate success: 413 (Request Entity Too Large).
at System.Net.Http.HttpResponseMessage.EnsureSuccessStatusCode() in /_/src/System.Net.Http/src/System/Net/Http/HttpResponseMessage.cs:line 172
at Keyfactor.Orchestrators.Services.HttpService.SendPostAsync[T](String uri, Object requestData, Dictionary`2 headers) in F:\BuildAgents\Default1\_work\24\s\src\OrchestratorServices\HttpService.cs:line 38
This indicates that the amount of data being returned on the job is greater than IIS on the Keyfactor Command server is configured to accept.
 Delete
Delete
The Delete function is used to fully remove an orchestrator from Keyfactor Command along with any associated jobs, certificate stores, and configured SSH servers. If you only wish to remove an orchestrator from view without this impact, you can mark it Disapproved instead. It will then be hidden from view unless you check the Include Disapproved checkbox.
If you wish to go forward with deletion, first disapprove the orchestrator. The Delete function can only be used on orchestrators that have been disapproved. Highlight the row in the orchestrator management grid and click Delete at the top of the grid or right-click the orchestrator in the grid and choose Delete from the right-click menu. You will be prompted to confirm that you really wish to delete this orchestrator and understand the consequences of this action. Type the orchestrator name and click Submit to complete the deletion.
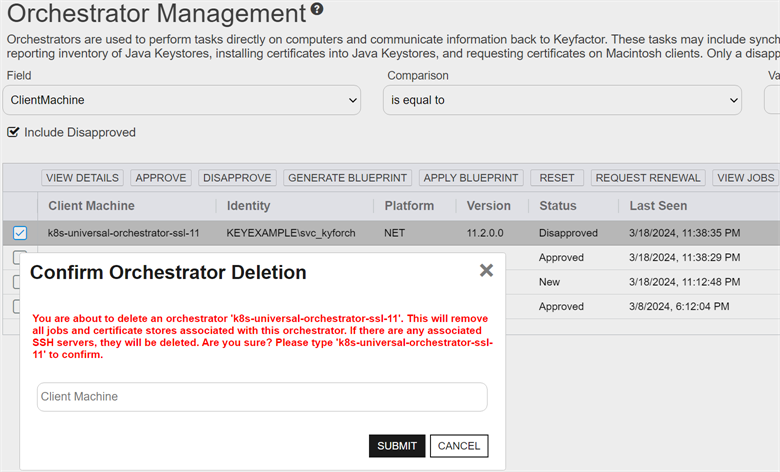
Figure 306: Deletion Confirmation for an Orchestrator